ADHD burnout occurs when you feel extreme emotional exhaustion from trying to keep up with everything you need to do. It may feel like you have run out of “fuel” and even feel ADHD paralysis — like you cannot do even simple tasks.
The good news is that recovery from ADHD burnout is possible. Let’s learn more about the signs to watch for, possible causes, and ways to deal with it.
Highlights
- ADHD burnout is not laziness; it is complete overwhelm on an emotional, mental, and physical basis.
- While burnout is common, when you have ADHD, burnout can happen more often and be more extreme.
- By reaching out to your support network, learning self-help skills, and getting help from medication when necessary, you can reduce the symptoms.
What Is ADHD Burnout?
Burnout represents a prolonged condition of
ADHD burnout isn’t an official diagnosis, and it shares many symptoms with general burnout. ADHD burnout means feeling physical and emotional exhaustion from trying to navigate life while managing ADHD symptoms. It can cause you to feel frustrated and unmotivated to do anything. This can result in extreme difficulty taking care of simple tasks, such as taking a shower, cleaning your house, or responding to texts or emails.
General burnout can also leave you feeling frustrated and unmotivated, but if you have ADHD, it results in a reduced ability to perform executive functions. This means that the common ability to juggle tasks, manage your time, organize your life, or focus your attention is already more difficult for you. This leads to burnout more often, and the ADHD burnout symptoms are more extreme.
Identifying ADHD Burnout
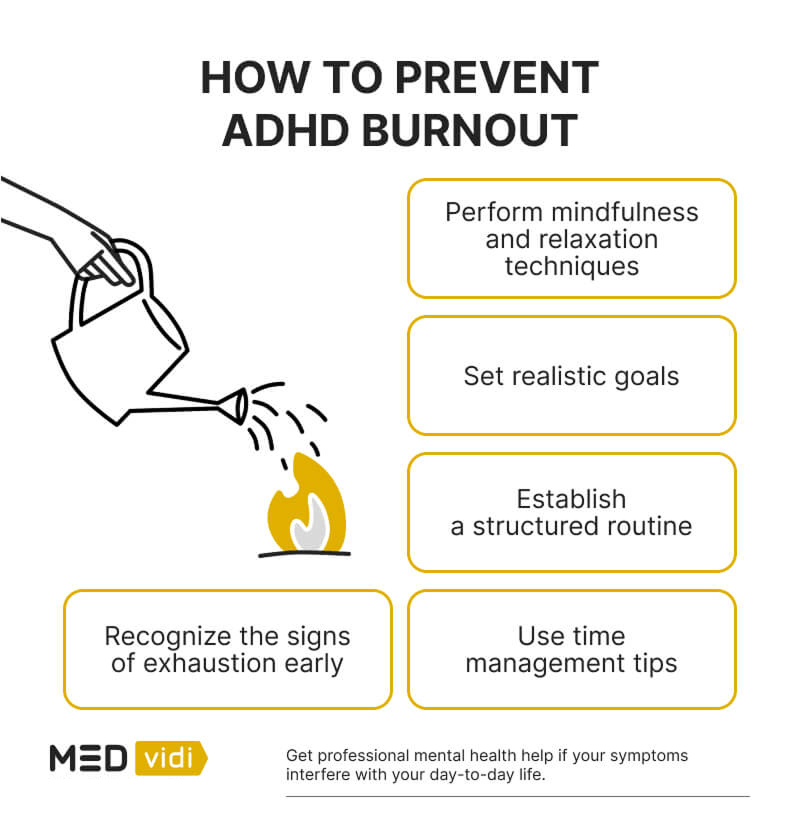
Once you learn to recognize what ADHD burnout feels like, it becomes easier to manage it and easier to avoid it happening again. While it can manifest differently from person to person, there are many signs that are common.
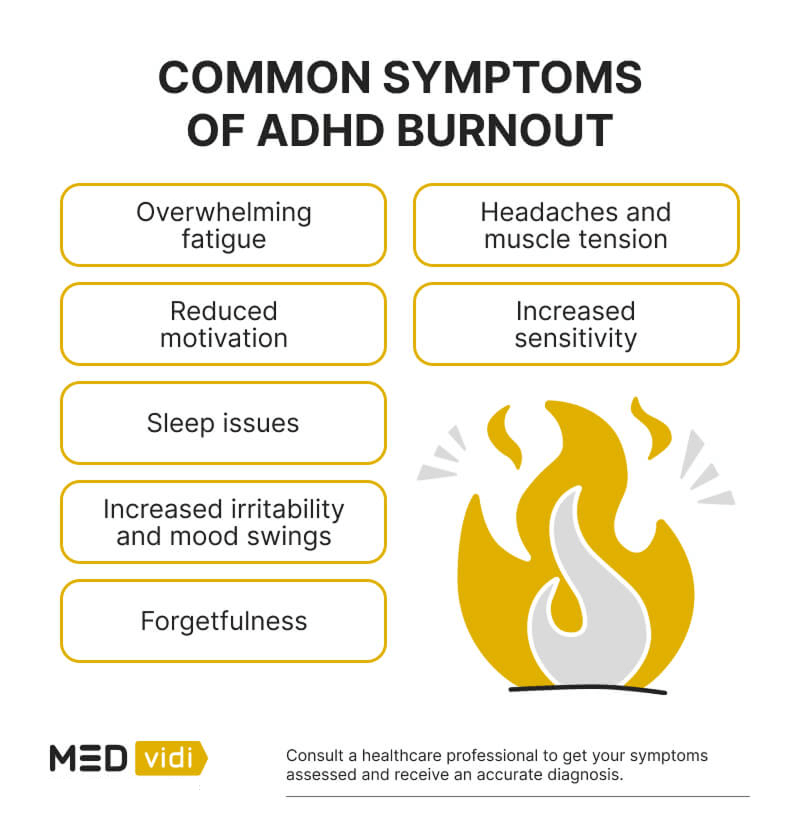
Remember that ADHD burnout symptoms can be complex and involve physical symptoms in your body, cognitive symptoms in your mind, and emotional ones as well. Some of them are listed below.
Emotional Symptoms:
- Little or no motivation
- Mood swings
- Little or no productivity
- Being overwhelmed easily
- Feeling emotional exhaustion
- Feeling irritable or more sensitive than usual
- Having a negative outlook on life
- Social burnout or withdrawing from your social circle
- Feeling sad, angry, or detached from loved ones
- Lower confidence and self-esteem
- Missing work or school days
- Performing poorly at work or school
- Feeling dissatisfied with your job
Physical Symptoms:
- Problems with digestion, such as an upset stomach, or a change in bowel habits
- Headache
- Tense muscles or achiness
- Problems sleeping well
- Losing your appetite
- Fatigue
Cognitive Symptoms:
- More trouble focusing on things than usual
- Problems remembering things
- More trouble completing tasks
- Increased difficulty concentrating

Differentiating ADHD Burnout From Depression
It’s important to remember that ADHD burnout and depression have many overlapping symptoms, such as trouble concentrating, tiredness, and low mood, and it can be difficult to tell the difference between the two. Studies show that ADHD and depression often occur together, which may make it even more difficult to tell what is depression and what is burnout.
Experts don’t agree on exactly what burnout is and how it relates to depression, but one way to tell the difference is that ADHD burnout is often specific to a certain frustrating or overwhelming situation or a project while depression may involve more generalized feelings of hopelessness and self-criticism.
ADHD Burnout Causes
If you’re ready to learn what causes ADHD burnout, know that just having ADHD can increase your risk for it. However, there are also other possible causes; let’s review them in more detail.
- Untreated ADHD symptoms: Research shows that
less than 20% of adults[2] with ADHD have been diagnosed and treated. If you don’t manage or treat your symptoms, the result can be frustration with yourself and low self-esteem, making you even more likely to burn out. - Constant strain on executive function: If you have ADHD, organizing your life, juggling tasks, and maintaining connections while staying on top of everything else is already strained. This stress can cause you to burn out sooner than others would.
- Overcommitment and people-pleasing behaviors: If you have ADHD, you may be more likely to feel stress when disappointing others. This can lead to people-pleasing behaviors or overcommitting to activities or social engagements. All of this extra strain and pressure may increase your risk of social burnout.
- ADHD masking: Suppressing or hiding your symptoms, also known as ADHD masking, can lead to burnout. Masking may include trying to come up with excuses for being late or disorganized, or trying to hide hyperactivity actions like fidgeting. Together, this can overload your executive functioning abilities.
- Perfectionism and procrastination: Both of these are more common in people with ADHD, which can lead to burnout through trying to be overly perfect, or procrastinating until you have too much work to do and too little time to do it.
- Lack of structure and routine: If you have ADHD, you may have difficulty creating routines because of impulsivity or organizational problems. These can lead to burnout through the stress of disorganization. Routine can help you prevent burnout.
- Insufficient social support: Studies show that people with ADHD have
less social support[3] , which can mean feeling more alone and having a harder time with burnout. - Emotional overload and mental fatigue: One of the hallmarks of ADHD is feeling overloaded mentally from reduced executive function. This constant feeling of overwhelm can be the jumping off point for burnout.
- Difficulty balancing work and personal life: Since executive dysfunction is at the root of ADHD, it’s common to have difficulty balancing all of the things you may need to do, which may cause burnout.
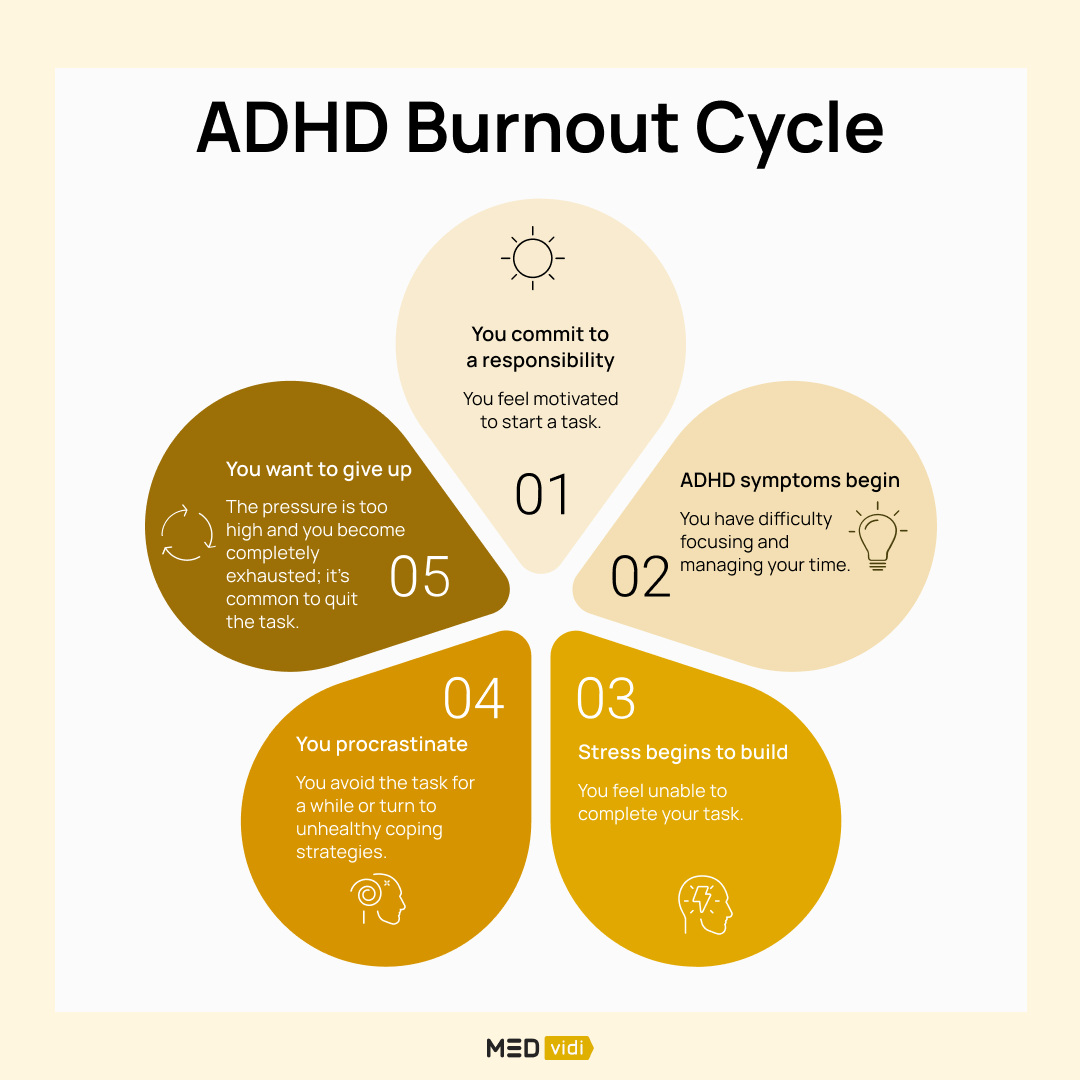
The ADHD Burnout Cycle
It’s common for people to experience a similar process before and during ADHD burnout. It often begins with a task that needs to be done, followed by intense focus, and then gradually losing the ability to concentrate and accomplish the task. While everyone is different, the ADHD burnout cycle often follows five stages.
- Stage One: You have a task to do so you commit to the responsibility. For example, you have an upcoming exam and need to gather materials and begin studying. You feel motivated and are ready to put all the effort you can.
- Stage Two: You begin the task but you also begin to experience ADHD symptoms, such as feeling disorganized, unfocused, and stressed. An example of this is that you may mismanage your time and feel stressed that you don’t have sufficient time to study.
- Stage Three: Because of the difficulty you’re experiencing in trying to maintain executive function, stress begins to build. So, you may feel unable to get organized enough to begin studying.
- Stage Four: The stress increases and the task starts to become overwhelming. You procrastinate in an attempt to lower your stress, but that just increases it. Consequently, you may avoid the task for a while or turn to unhealthy coping strategies, such as drinking alcohol or doomscrolling on your phone.
- Stage Five: The situation feels out of control and you are ready to give up. An example may be that you feel the pressure is too high, you become completely exhausted and you end up giving up on the idea of studying for the exam.
Impact of ADHD Burnout on Daily Life
Experiencing ADHD burnout can significantly impact your life on a day-to-day basis. You may be less productive, which may result in poor performance at work, falling behind on household chores, or having trouble communicating with your loved ones. The constant overwhelm may cause you to put in less effort in your personal relationships, possibly leading to hurt feelings or tension within your social circle. In order to help reduce the negative impact of these circumstances, it’s important to learn how to identify the initial stages of the burnout cycle and to learn tips on how to recover from ADHD burnout.
10 Recovery Tips If You Have ADHD Burnout
In order to recover from the ADHD burnout cycle, recognize what caused it in the first place. It may be the result of being overworked, or a problem with managing your time efficiently. Whatever the cause, be kind to yourself. Look for the signs of ADHD burnout and remember to use these tips:
- Rest and self-care: Itэs important to schedule down time for yourself as often as you can. Take time to rest and for self-care, which may include time in nature, extra sleep, or time with a loved one. Often, rest can help you get out of ADHD burnout.
- Develop a comfortable routine: Routines can help you manage your time and enable you to get everything done. Some routines, such as a bedtime routine, can set you up for a good nightэs rest.
- Develop healthy habits: Eat a healthy breakfast to start the day, set aside time for exercise, or put your phone away before bedtime. These habits may help you feel good enough to accomplish everyday tasks and help overcome ADHD burnout.
- Manage ADHD symptoms: Talk with your doctor or a therapist to help you find a way to manage ADHD symptoms which may reduce the likelihood that burnout will happen again. It may help you to better recover from ADHD burnout.
- Create a supportive environment: It may help to explain your challenges to those who are closest to you in an effort to gain their help or understanding. When you feel supported and understood, you may be able to navigate your life and responsibilities with less stress.
- Implement stress-management and relaxation techniques: Try different tools to find those that work for you. These techniques may include meditation, talking to a trusted friend, spending time in the sunshine, or listening to music.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness can be powerful to help ADHD burnout. Focus on what is happening, how you are reacting to it, and don’t judge yourself for your reactions. Use it as a learning experience.
- Utilize time management and prioritization techniques: Set timers on your cell phone, use a paper planner, or find other techniques to stay on top of everything you need to do.
- Set realistic goals and expectations: Be kind to yourself and remember ADHD burnout is difficult. Don’t expect everything to be perfect.
- Seek professional help: Doctors and therapists are available to help overcome ADHD burnout; they can offer coping strategies, tools, and medication, if needed. At MEDvidi, you can get ADHD treatment online, accessing professional care from the comfort of your home.

Additional Tips:
- Be patient and understanding with yourself. Recovery from the ADHD burnout cycle takes time and effort. If you don’t give yourself the time you need to get over ADHD burnout, then you’ll be more likely to experience it again.
- Set realistic goals and celebrate small victories. Acknowledging the wins can help you feel good about your efforts and may help you avoid burnout.
- Avoid comparing yourself to others. The symptoms of ADHD vary, and what helps one person may be less effective to the other; so, it’s fine if your experience is different.
- Seek support from your family, friends, or a support network. Others may not understand what ADHD burnout feels like, but having people around you who understand and support you can make a big difference.
Conclusion
If you are living with ADHD, then experiencing burnout can be more severe and longer-lasting than it is for someone without this condition. Over time, you can learn what the causes are, how to spot the symptoms, and how to successfully avoid burnout — or at least reduce its impact — in the future. Surrounding yourself with a good support system can make all the difference; also, if the symptoms of ADHD prevent you from leading the life you are used to, book an appointment to see a medical provider to get a treatment plan for ADHD.
FAQ
Can ADHD make burnout worse?
Yes. While everyone experiences burnout sometimes, people living with ADHD are more likely to experience it, and when it happens, it can be more severe.
How long does ADHD burnout last for?
How long the ADHD burnout cycle lasts depends on how severe it is. Burnout can last for a few days, weeks, or even months. Seeking treatment and support can help reduce the burnout time.
How to recharge after ADHD burnout?
Try different ways to recharge after a burnout, including spending time with supportive friends or family, taking time to rest, doing something that you love, or getting some extra sleep. Recharging afterward can help you avoid burnout again.
Are women with ADHD more vulnerable to burnout than men?
Yes. Women with ADHD are more likely to experience anxiety and depression along with ADHD, which may lead to a higher likelihood of burnout. Hormonal changes, such as during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause may influence the situation as well.
What does ADHD burnout look like in women?
Signs of ADHD burnout in women may look similar to signs in men and may include fatigue, cynicism, and being self-critical.
How to help someone with ADHD burnout?
Don’t judge them for their situation. Offer help and support, proceed with kindness to help them get out of ADHD burnout, and encourage them to seek professional help if symptoms are severe.













