Specific phobias are disorders characterized by extreme, overwhelming, and irrational fears of living creatures, places, situations, or objects. These specific phobias are persistent and cause mental and physical reactions. Phobias disrupt the normal life of a person.
According to the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) prevalence rates data, approximately
According to
Specific Phobia: DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
It is natural to have common fears or anxiety in some situations, like giving a public speech. There is a difference between these short-lived symptoms and phobias.
All phobias have common characteristics, so the following criteria should be met to make a diagnosis:
- A person goes out of his/her way to avoid the source of the phobia.
- An encounter with an object or situation always causes extreme distress.
- Extreme and immediate response when presented with the source of fear.
- An encounter with the source of phobia triggers out-of-proportion, irrational, and persistent fear not representative of the actual threat.
- The disorder disrupts a patient’s daily life.
- A doctor rules out other disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder or agoraphobia as the cause of the phobia.
- The specific phobia symptoms have lasted for at least six months.
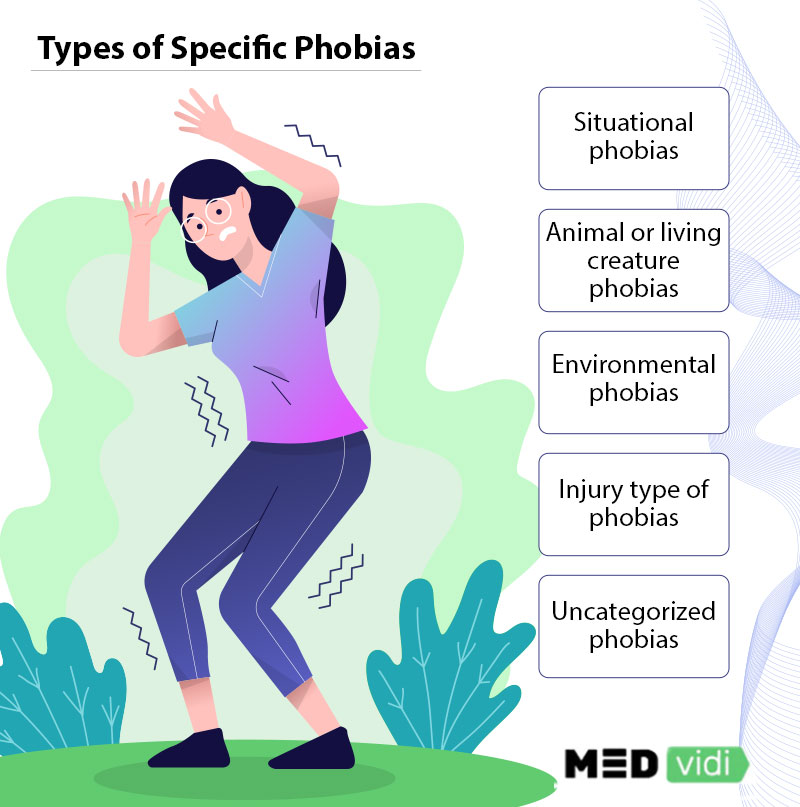
Types of Specific Phobias
There are five types of different
- Situational phobias. Specific circumstances trigger the anxiety. These could be phobias like:
- Acrophobia (fear of heights)
- Claustrophobia (fear of being in confined or constricted spaces)
- Gephyrophobia (fear of bridges and tunnels)
- Animal or living creature phobias. These are fears triggered by insects, animals, or other living creatures. Some options in the list of phobias in this case include:
- Entomophobia (fear of insects)
- Ophidiophobia (fear of snakes)
- Arachnophobia (fear of spiders)
- Environmental phobias. These are fears of natural features or natural occurrences such as:
- Aquaphobia (fear of water)
- Astraphobia (fear of thunder and lightning)
- Nyctophobia (fear of the dark)
- Injury type of phobias. Physical harm, injury, or blood triggers such as:
- Dentophobia (fear of dentists)
- Trypanophobia (fear of needles)
- Hemophobia (fear of blood)
- Uncategorized phobias. The phobias do not fit in the other four clusters. These are fears of experiences or situations like:
- Emetophobia (fear of vomiting)
- Hypochondria (fear of getting sick)
- Trypophobia (fear of holes)
Causes of Specific Phobias
Several factors can contribute to the development of the disorders, including:
- Brain functioning. Changes in brain functions may ignite the development of phobias.
- Genetic and environmental factors. It is possible to inherit phobias from the family lines. A person living with people who have specific disorders is likely to learn the same behaviors.
- Past experiences. Most phobias develop from negative experiences. For example, a snake bite encounter may ignite ophidiophobia.
- Temperament. People with personality traits of neuroticism and behavioral inhibition are more likely to develop such disorders.
Treatment and Management of Specific Phobias
Since most people with phobias are aware of their disorder, specific phobia treatment and management are often successful. The treatment is usually tailor-made to suit a patient’s case, and psychotherapy is the first-line choice.
Psychotherapy Interventions
Various therapeutic approaches are used to treat specific phobias. The most common interventions include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Behavioral/Exposure therapy
Sometimes, a doctor may recommend a combination of psychotherapy and medical treatment for the best results.
Medication Treatment
Effective pharmacological treatments include:
- Antidepressants such as serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI) help to balance serotonin levels. Serotonin is the neurotransmitter that regulates a patient’s mood. Tricyclic antidepressants such as Anafranil or Clomipramine are also used to treat some phobias.
- Beta-blockers reduce physical reactions to a phobia.
- Benzodiazepines reduce anxiety symptoms.
Specific phobia medication may have mild or severe adverse reactions in the patient. In case of severe side effects, a patient should seek a medical review from the doctor.
Conclusion
Specific phobias are common disorders that may hamper a person’s everyday life. Still, they are easy to diagnose since patients are aware of their problems, and treatment is usually successful. If you find yourself struggling with any phobia, contact MEDvidi doctors to get treatment and live a productive life.










