Once a person hears the diagnosis of “attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder” (ADHD), they might think that pharmacological treatment is the only option. But although stimulant medications (including methylphenidate and amphetamine) are the core interventions for managing this condition, there are other strategies too.
Given that ADHD cannot be cured completely, a person should rely on different types of self-support. Medications can aid well for quick help. But for long-term results, psychotherapy and a variety of natural alternative treatments for ADHD will be beneficial too. According to the MTA Cooperative Group Study, using natural therapies like lifestyle modification, brain training, and behavior therapy to complement ADHD medications provides better results than drugs alone. So, let’s delve into the details of the diversity of alternative treatment options.
Want to manage ADHD symptoms effectively? Ask our doctors for a personalized treatment plan.
ADHD Treatment Overview
Currently, there are no set parameters for predicting individual patients’ responses to ADHD treatments. Monitoring symptoms is the only way to determine if a particular therapy is helpful. Noteworthy, you’ll have to be open to numerous changes in diet, exercise, sleep, and more before finding which treatment works best.
Your therapist will require you to keep a symptom log detailing improvements and setbacks before recommending new approaches.
Alternatives to ADHD Medications
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Generally, CBT aims to modify specific thought patterns that cause maladaptive behavior. The difficulty in accomplishing tasks by adults with ADHD might emanate from irrational thoughts. CBT challenges the individual to examine the evidence of such ideas with the aim of correcting ADHD symptoms.
According to the
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential in enhancing brain and nerve cell function. However, the body cannot manufacture these fatty acids, which must be acquired through diet. Foods such as salmon and mackerel, as well as supplements and vitamins, help boost your omega-3 levels and promote brain function. Fish oil contains two types of omega-3 acids: docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). The latter is more beneficial than the former. Thus, when buying supplements, consider those with higher levels of EPA than DPA.
A 2018 study showed that omega-3 fatty acids help alleviate symptoms in individuals with ADHD, while another
Protein-rich Diet
Proper nutrition is a powerful tool for managing ADHD in adults. According to a
Other foods for managing ADD include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. When using ADD alternative treatment, avoid excessive fat consumption as they interfere with drug absorption and effectiveness. Therefore, most experts recommend diets consisting of proteins and complex carbohydrates, as described.
Self-help tips may not be enough for some patients. Contact MEDvidi today to get personalized ADHD treatment.
Exercise for ADD
Exercise enhances brain functions and improves mood, emotions, and sleep. When people exercise, the chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, increase. These substances help you to focus better, reducing inattention. Physical activities, including walks and skill-based exercises like ballet or martial arts, offer great benefits in ADHD management. Yoga and other aerobic exercises reduce the symptoms like impulsivity and inattention and improve executive functions.
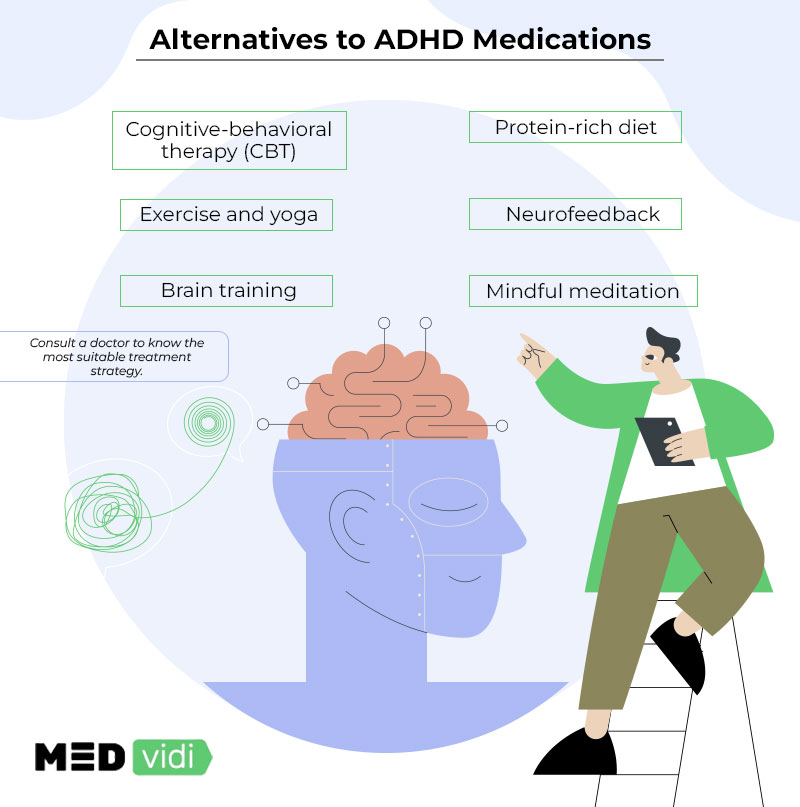
Brain Training
Brain training programs for ADHD and ADD continue to grow in popularity as they are available on computers, smartphones, and other devices. The programs promise to improve functions, attention, and memory, which are usually disordered in individuals with ADHD. While the tasks might resemble video games, they are designed to stimulate particular brain functions.
With technological advancement, a brain training method called neurofeedback is emerging as a potential alternative ADHD treatment for adults. The therapist will ask you to perform particular cognitive tasks while wearing an electrode-lined cap. Usually, a session lasts about half an hour. The treatment aims to help patients produce brain signals and connections associated with focus.
A
Ask a doctor about beneficial routines you can implement to improve ADHD symptoms.
Mindful Meditation
Individuals with ADHD can learn to manage stress, strengthen self-regulation, and develop positive emotions through mindfulness meditation. This treatment plan helps you stay in the moment by meditating silently and increasing self-awareness as you perform daily tasks. According to the
Conclusion
Medications are the core tools for treating ADHD in adults. That said, individuals who prefer other methods to the medical route can pursue alternatives to ADHD medication for adults, including nutrition, exercise, brain training, and neurofeedback. Notably, these alternative therapies require additional research to prove their effectiveness. Your therapist can recommend combining two or more treatments to complement ADHD medications. To know more about which treatment strategies will suit your situation best, contact MEDvidi doctors today.