Their inclusion does not guarantee they will be prescribed to any individual, as treatment decisions are ultimately at the discretion of healthcare providers. Healthcare providers may prescribe other medications or recommend non-pharmacological treatment based on the patient’s unique health circumstances and needs. Read more
Highlights
- Adderall and Ritalin are both used as central nervous stimulants to treat ADHD and narcolepsy, as well as numerous other off-label conditions.
- Adderall’s active ingredient is a mixture of amphetamine salts and Ritalin’s active ingredient is methylphenidate.
- Both medications are available as brand or generic and come as immediate-release tablets or extended-release capsules.
- Adderall and Ritalin both have risks of serious side effects that should be thoroughly understood before starting treatment. They include heart issues, movement disorders, serotonin syndrome, and abuse or dependence.
Adderall and Ritalin are stimulants commonly prescribed for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). These medications are effective in managing impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattentiveness. They also help increase energy and concentration levels while positively affecting a person’s mood.
The ultimate goal of both Ritalin and Adderall is the same — to control ADHD symptoms. However, there are some subtle differences in their functioning, doses, uses, cost, and side effects that you should know. This article will cover all the crucial points about Ritalin vs. Adderall and clear all your doubts with up-to-date information on these medications.
Ritalin vs. Adderall for ADHD
Both Adderall and Ritalin are primarily indicated for ADHD. In addition, they are also approved by the FDA to treat narcolepsy.
Adderall and Ritalin are both effective in controlling and managing all types of ADHD symptoms in about
According to a
The usual starting dose of Adderall for ADHD is between 5 mg to 40 mg once or twice a day, taken in the morning and at noon. On the other hand, Ritalin is usually prescribed for ADHD as 20 mg or 30 mg tablets two to three times a day at the start, to be taken in the morning, noon, and afternoon. In contrast, Adderall XR and Ritalin LA can be taken once daily as their effects last longer.
Note: Dosages are determined separately for each patient, depending on their therapeutic needs, and can change with treatment. Always contact your healthcare provider for any questions on the dosage.
Ritalin vs. Adderall: Differences and Similarities
Similarities
There are a host of similarities between Adderall and Ritalin. Both medications:
- Belong to the class of drugs called CNS stimulants;
- Are listed as Schedule II controlled substances by the FDA, making them highly controlled substances;
- Are approved by the FDA for treating ADHD and narcolepsy;
- Should be stored at room temperature between 68℉ and 77℉;
- Are prescribed for short-term or long-term treatment, depending on the patient’s symptoms;
- Have similar side effects;
- Have a high potential for abuse and withdrawal side effects.
Differences
Chemical Composition
The main difference between Adderall and Ritalin is their active ingredient. Adderall’s is a mixture of four amphetamine salts, and Ritalin contains methylphenidate hydrochloride.
Mechanism of Action
Amphetamines (Adderall) and methylphenidate (Ritalin) work by increasing the levels of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain. Among other mechanisms, they reduce the reabsorption of these neurotransmitters, so their effects last longer. However, Ritalin and Adderall achieve these effects in different ways, and each medication has its unique functions along with shared ones.

Duration of Action
Another important difference between Adderall and Ritalin is their duration of action, or how long their effects last.
- Ritalin is a short-acting medication with a half-life of 2 to 3 hours (the amount of time it takes a medication’s active component to reduce by half).
- Adderall has a longer half-life of about 6 hours.
As a result, their doses are adjusted accordingly. Adderall is typically prescribed in a single or twice daily dose, while Ritalin requires multiple doses throughout the day to sustain its therapeutic effects.
However, now these medications also have slow-released versions available, namely Adderall extended-release (Adderall XR), Ritalin sustained-release (Ritalin SR), and Ritalin extended-release (Ritalin LA). These medications lower the multiple dosing issues as they remain effective in the body for a longer time. The effects of Adderall XR last 10 to 12 hours, whereas Ritalin LA manages the symptoms for 8 to 10 hours.
Follow your physician’s instructions and never exceed the prescribed dose.
Use in Children
Adderall is intended for use in children ages 3 and older. Ritalin is intended for children over 6 years old.
Long-term use with either medication has not been well studied and should be done with extra caution. There is a specific risk for long-term
Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of Ritalin and Adderall varies depending on whether you are getting the generic or brand version. It also depends on your insurance plan and coverage of these medications. For example, 60 tablets of generic Adderall of 5 mg strength are priced from $17.33 to $105.70. The same supply of a brand version costs from $777.69 and $937.19. It is possible to save using coupons.
The generic version of Ritalin (methylphenidate) costs from $26.98 to $117.10 for 60 tablets of 5 mg strength. The same supply of a branded version of Ritalin costs from $127.71 to $149.76. Again, coupons are available for this medication. Also, insurance plans, including Medicare, usually cover the generic versions of Adderall and Ritalin. For complete details about the coverage, contact your insurance provider.
Note: These are the average prices of Adderall and Ritalin, and the final price of the medication may be higher or lower depending on your insurance plan and pharmacy.
Currently, some strengths of the generic form of immediate-release Adderall are backordered. Additionally, generic extended-release Ritalin is also on backorder. When there are shortages of certain strengths or forms, work with your healthcare provider and pharmacy to identify solutions.
Some options could be switching to the brand versions, although this often requires further authorization from the insurance and leads to higher copays. Another option includes a prescription for higher-dose tablets that are broken in half to achieve the proper amount of the medication. You can visit
Summary of Main Ritalin and Adderall Features
Feature | Ritalin | Adderall |
Drug class | CNS stimulant | CNS stimulant |
Mechanism of action | Increases neurotransmitter levels | Increases neurotransmitter levels |
Chemical composition | Methylphenidate | Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine salts |
Available forms | Ritalin Ritalin LA | Adderall Adderall XR |
Available dosages | Ritalin: 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg tablets Ritalin LA: 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, and 40 mg capsules | Adderall: 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg tablets Adderall XR: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, and 30 mg capsules |
Age of use | 6 years and older | 3 years and older |
Duration of action | Ritalin — 2 to 4 hours Ritalin LA — 8 to 10 hours | Adderall — 4 to 6 hours Adderall XR — 10 to 12 hours |
Ritalin vs. Adderall Side Effects and Risks
Side Effects
The side effects of Ritalin and Adderall are very similar because they are both stimulants and work similarly in the body. Remember, their intensity can differ from one person to another.
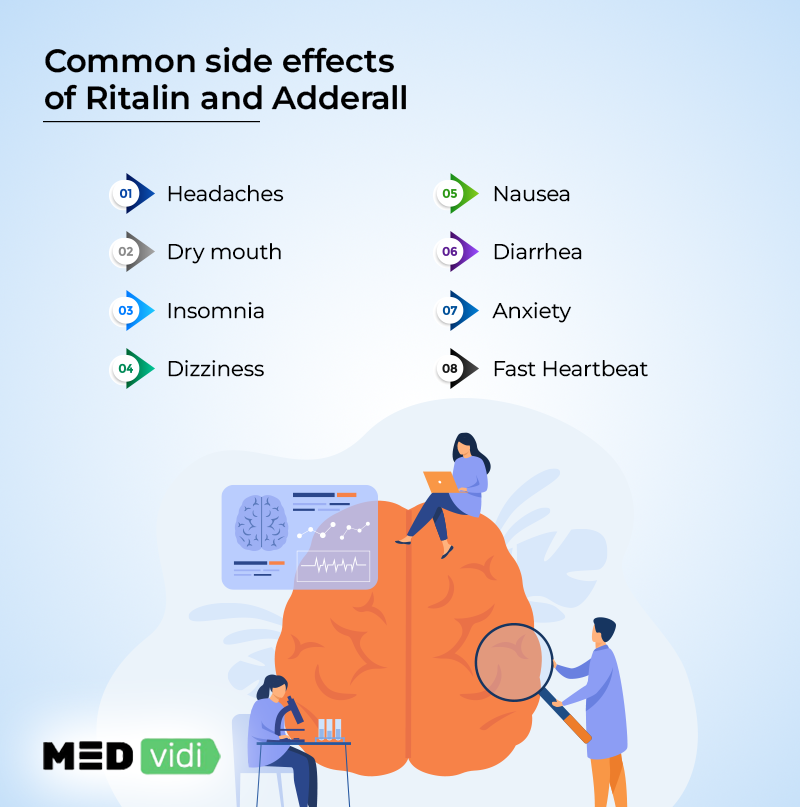
Common side effects of Ritalin and Adderall:
- Headaches
- Dry mouth
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Anxiety
- Agitation
- Palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fast heartbeat
Less common, serious side effects of Ritalin and Adderall:
- High blood pressure
- Heart problems
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Severe anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Tics
- Tourette syndrome
- Seizures
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
- Serotonin syndrome
- Exacerbation of glaucoma
- Exacerbation of hyperthyroidism
- Bruxism (abnormal clenching of teeth)
- Formication (abnormal skin sensations)
- Emotional lability (exaggerated changes in emotions)
Note: This is not a complete list of side effects caused by Ritalin and Adderall. For any queries related to the side effects, please contact your doctor and pharmacist.
Risks
Heart Issues
Stimulants such as Ritalin and Adderall increase the heart rate and blood pressure. This puts the patients at extra risk of having a heart attack or stroke, especially in those who already have a pre-existing heart condition or high blood pressure. According to a
Drug Overdose
At normal treatment doses, Ritalin and Adderall usually do not cause serious complications. However, due to their potential for abuse, there is
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Ritalin and Adderall have a high risk of drug abuse in people who take them at high doses for a long time for non-medical reasons. It can cause physical and psychological dependence, which can spiral into addictive behavior.
Drug Interactions of Ritalin and Adderall
Ritalin and Adderall similarly interact with many drug classes. Stimulants increase the plasma levels of medications by decreasing their metabolism. These include tricyclic or tetracyclic antidepressants, phenytoin, warfarin, primidone, etc. They may also decrease the effectiveness of certain antihypertensives such as lisinopril, losartan, etc. Here is a list of some of the common drug interactions of stimulants.
|
Drug |
Drug Class |
Possible Reaction with Adderall and Ritalin |
|
Isocarboxazid Phenelzine Selegiline |
MAOIs |
Hypertensive crisis |
|
Halothane Isoflurane Desflurane |
Anesthetic agents |
Cardiac instability (irregular rhythm) |
|
Amlodipine Lisinopril Losartan |
Antihypertensives |
Decreased efficacy of antihypertensives |
|
Bisoprolol Metoprolol |
Beta-blockers |
Cardiac problems |
|
Trazodone Fluoxetine Sertraline |
Antidepressants |
Serotonin syndrome |
Adderall may also cause problems in measuring corticosteroids in the body as they may elevate their levels.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all the possible drug interactions of Adderall and Ritalin. Please contact your doctor or pharmacist for further details.
Contraindications of Ritalin and Adderall
Adderall and Ritalin both have contraindications, or instances that would make using the medication unsafe for a patient. If any of the following conditions apply to you, you should alert your healthcare provider, as taking Ritalin or Adderall may be unsafe. These contraindications include:
- Having structural cardiac defects such as patent foramen ovale (PFO) and atrial septal defect (ASD).
- Narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Moderate to severe substance abuse disorder.
- Past known allergy to stimulants.
- Using MAOIs currently or discontinued their use within the last 14 days.
- Having been diagnosed with psychotic disorders like schizophrenia because stimulants can precipitate maniac symptoms.
- Severe tics or Tourette syndrome.
- Unstable hypertension. Blood pressure should be controlled first before starting stimulant medications.

Final Words
Adderall and Ritalin are potent stimulant medications for ADHD treatment and some other medical conditions. There are minor differences in their cost, forms, dosages, and drug interactions. They are highly controlled medications due to their risk of misuse. However, when used in therapeutic doses under a doctor’s guidance, they effectively control ADHD symptoms in most cases.
Our medical professionals are experienced in creating personalized treatment plans for adults with ADHD. For any questions related to ADHD medications, including Ritalin and Adderall, you can book an appointment and talk to one of our healthcare providers online.
Ritalin vs. Adderall: FAQs
Which medication is more effective, Ritalin or Adderall?
Can you take Ritalin and Adderall together?
Can you switch from Ritalin to Adderall?
Which is the stronger medication, Ritalin or Adderall?
Generally, Adderall is twice as
Can you use Ritalin or Adderall during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
The use of Ritalin and Adderall during













