Highlights
- Off-label medications for anxiety are used when first-choice medications don’t work or cause intolerable side effects.
- These medications may have research backing their use for anxiety, even though they aren’t FDA-approved for it.
- Common off-label medications for anxiety include certain SSRIs (though some SSRIs are FDA-approved for anxiety), anticonvulsants, and beta-blockers.
- It’s essential to consult with a medical provider before using off-label medications to ensure safety and effectiveness.
When you live with anxiety, it’s common to start with first-choice treatments, such as FDA-approved medications. However, these don’t always work for everyone. You may experience side effects or find that the medication doesn’t fully manage your symptoms. When this happens, your healthcare provider may consider using off-label medications for anxiety treatment.
In this article, we’ll go through all of the medications that can be used off-label to treat anxiety, and what this might mean for your treatment plan.
What Are Anxiety Disorders?
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Persistent, excessive worry about various aspects of daily life.
- Panic Disorder: Sudden, intense bouts of fear or discomfort, often with physical symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Intense fear of social situations, often linked to fears of being judged or embarrassed.
- Specific Phobia: Extreme fear of a particular object or situation, such as spiders, heights, or flying.
- Separation Anxiety Disorder: Excessive fear or anxiety about being separated from loved ones.
What “Off-Label” Means
When a medication is
Approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can be a long and complex process with stringent requirements; it requires large clinical trials and robust evidence. However, off-label medication could have some research supporting its effectiveness, even though it’s not FDA-approved. Usually, it means that the studies supporting it aren’t large enough for approval.
Medical providers will almost always start with FDA-approved medications because they know they’re safe and effective for most people. But for some, those medications don’t work, or might come with intolerable side effects. In those cases, providers can try off-label medications to see if they make a bigger difference. These are prescribed if they’ve been found in research to be helpful for that condition.
What Is FDA Approval?
The Food and Drug Administration is a regulatory body that ensures the safety, efficacy, and security of human medication, veterinary drugs, and medical, biological, and cosmetic products.
When a
FDA labels include information about safety, as well as the specific conditions the medication is approved for. So, prescribing something off-label means that the FDA says it’s safe and has approved it for other conditions — just not the one you live with. It doesn’t mean that the medication hasn’t been approved by the FDA at all, or that it’s unsafe.

FDA-Approved vs. Off-Label: Key Considerations
|
FDA-Approved Anxiety Medications |
Off-Label Anxiety Medications |
|
Specifically approved for anxiety disorders |
Approved for other conditions but often used for anxiety |
|
Backed by large clinical trials specifically focused on anxiety treatment |
Often supported by smaller studies or clinical experience |
|
First-choice treatments for many patients |
Used when first-line options fail or cause intolerable side effects |
|
Usually covered by insurance when prescribed for anxiety |
Insurance coverage may be less certain |
|
Dosing and usage guidelines well-established |
Dosing for anxiety may vary and rely on physician judgment |
Off-Label Anxiety Medications
There are many off-label medications that can be prescribed for people with anxiety disorders. Here are some of the most common categories.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Some SSRIs — a common type of antidepressant medication — are
Examples of SSRIs that are prescribed off-label for anxiety include:
Tricyclic Antidepressants
Some examples include:
- Amitriptyline (Elavil)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are usually prescribed for patients with heart conditions such as high blood pressure. However, they can also be effective in the treatment of the symptoms of anxiety.
Examples of beta blockers that can be used off-label for anxiety include:
- Atenolol (Tenormin)
- Propranolol
(Inderal)[7]
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are one of the oldest depression treatment medications on the market. MAOIs may be prescribed off-label to alleviate social anxiety disorder and panic disorder symptoms.
MAOIs include:
- Emsam (Selegiline)
- Marplan (Isocarboxazid)
- Nardil (Phenelzine)
- Parnate (Tranylcypromine)
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are usually used to treat allergies. But they often come with sedative side effects, which can make them useful off-label for anxiety disorders. They can also help you sleep. One antihistamine is FDA-approved for anxiety (hydroxyzine, brand name Vistaril). Some providers may also prescribe OTC antihistamines, like Benadryl, to treat anxiety.
Antihistamines come with side effects like sedation and dizziness. Don’t take them for anxiety without consulting your mental health provider.
Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants are typically used to treat epilepsy and other seizure disorders. But they are used off-label to treat many different mental health conditions, including bipolar disorder and anxiety. They often work to reduce physical symptoms of anxiety, like shakiness.
Some examples of anticonvulsants that can be used off-label to treat anxiety include:
- Gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Valproate (Depakote)
Antipsychotics
Lastly, antipsychotic medications are sometimes used to help certain anxiety disorders. These medications are primarily used to treat psychotic disorders like schizophrenia. Only one antipsychotic medication is approved for anxiety. But many people get them prescribed off-label — one review found that
Some antipsychotics that can be used off-label for anxiety include:
- Olanzapine
- Aripiprazole
- Risperidone
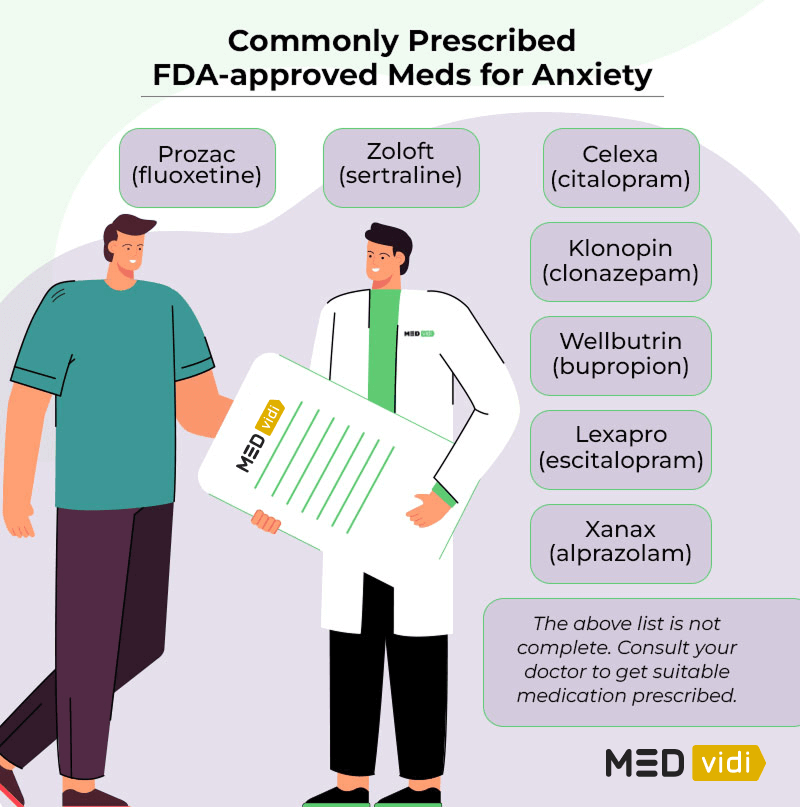
FDA-approved Medications for Anxiety
Here’s a list of the medications that are FDA-approved for anxiety disorders specifically.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
The SSRIs that are FDA-approved for generalized anxiety disorder (the most common type of anxiety), on top of other types of anxiety, are:
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Escitalopram (
Lexapro[9] )
In addition, other SSRIs are FDA-approved for other types of anxiety disorders, including:
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are sedative medications that alleviate physical symptoms of anxiety disorders, such as excessive sweating and tense muscles. Benzodiazepines are prescribed for short-term use only since they can be highly addictive and come with the risk of abuse. That is why you should never rely on benzodiazepines alone to treat anxiety disorders — talk therapy or other additional treatment options are likely to be recommended.
The benzodiazepines that are FDA-approved to treat anxiety (including panic attacks) are:

Serotonin-norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are a type of antidepressant that works by altering the levels of different chemicals in your brain. They’re considered safe and come with relatively few side effects compared to some other anxiety medications. They were designed to treat depression, but most of the common ones are approved for generalized anxiety. Specific brand names include:
- Venlafaxine (Effexor)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
Buspirone
Buspirone (BuSpar) is an anti-anxiety medication that’s FDA-approved for generalized anxiety disorder. It has fewer side effects than some other medications, and there is no risk of addiction.
Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine is the only antihistamine that’s
Trifluoperazine
Trifluoperazine is the
Risks and Safety
Just because a medication isn’t FDA-approved for anxiety doesn’t mean it’s not safe — and vice versa. For example, taking benzodiazepines, an FDA-approved class of medications for anxiety, long-term can come with a significant risk of addiction and dependence. On the other hand, many people have safely taken off-label medications for their anxiety symptoms for years.
The important thing is to consult with a licensed healthcare provider to weigh the risks of each medication against its benefits. Most medications can come with some side effects, but working with a professional helps ensure you choose the best option for your symptoms.
Takeaway
Anxiety disorders can be treated with both FDA-approved and off-label medications. While FDA-approved anxiety medications are generally the first choice, off-label ones might be a good alternative when other treatments fail or cause too many side effects. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to explore the options that will work best for you.
At MEDvidi, we understand that managing anxiety requires a tailored approach. If you’re struggling to find the right treatment, our team of licensed healthcare providers is here to help you explore both FDA-approved and off-label anti-anxiety medications. Book your appointment today to see a medical professional in 24 hours.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which medications are FDA-approved for GAD?
Some of the FDA-approved medications for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) include:
- SSRIs (Paxil, Lexapro)
- SNRIs (Effexor, Wellbutrin)
- Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Ativan, and others)
- Buspirone













