According to recent data, more than
Many treatments are available for anxiety, including medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes. Effexor is one medication used to treat anxiety disorders. It is available in extended-release formulas such as Effexor XR. The immediate release version (Effexor) has been discontinued but is still available in generic form. But is Effexor good for anxiety?
Read on to learn more about Effexor for anxiety and depression and the alternatives to Effexor for anxiety.
Does anxiety prevent you from doing the things you like? Consult MEDvidi doctors to get personalized support.
What is Effexor
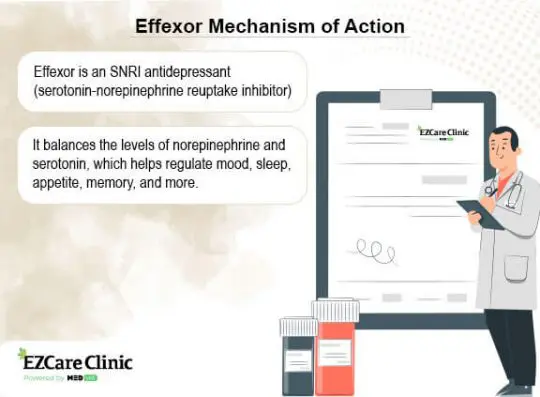
Effexor (venlafaxine) is an antidepressant belonging to a group of substances called serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). SNRIs boost norepinephrine and serotonin, which help the brain maintain the balance of those neurotransmitters.
Effexor is officially approved to treat major depressive disorders, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder in adults.
Studies have shown that
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Migraines and tension headaches
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Fibromyalgia
How Does Effexor Work for Anxiety
Three basic molecules, chemically called monoamines, are involved in mood regulation. They primarily function as neurotransmitters, transmitting nerve signals to their respective receptors in the brain. Effexor works by affecting the following neurotransmitters:
- Norepinephrine: Influences motor function and alertness and helps regulate blood pressure and heart rate.
- Dopamine: Plays an essential role in motivation, decision-making, and arousal.
- Serotonin: Regulates appetite, mood, sleep, memory, social behavior, and desires.
Simultaneously increasing norepinephrine and serotonin levels can be useful if one has depression. In people with stress and depression, the availability of these neurotransmitters in the brain and body is very low. Antidepressants such as Effexor boost the availability of these neurotransmitters, thus alleviating anxiety.
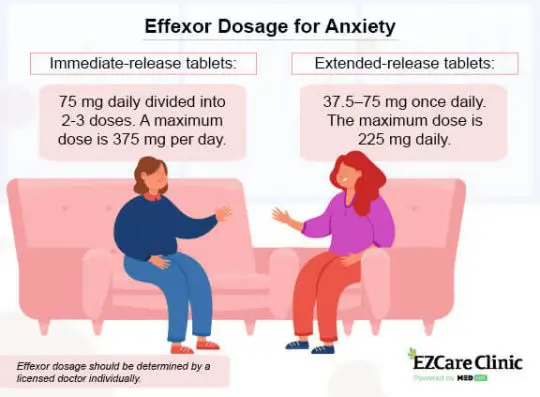
Proper Effexor Dosage for Anxiety
Effexor comes in oral tablets (generic version) and extended-release capsules that reduce the number of daily intakes. It fits a long-term application. Effexor XR is not a controlled medication.
Venlafaxine is available in the following dosages:
- Immediate-release: 25 mg, 37.5 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg and 100 mg
Treatment with immediate-release oral tablets starts at 75 mg daily, given in two or three doses. The dosage can be increased to 150 mg, with a maximum dose of 375 mg per day. - Extended-release: 37.5 mg, 75 mg, and 150 mg
The typical starting dose of the extended-release (Effexor XR) oral tablet is 75 mg daily, taken in the morning or evening. This dose can be increased by 75 mg every four days until reaching the maximum dose of 225 mg daily.
A healthcare provider will determine the dosage based on a patient’s age, symptoms, medical condition, and response to treatment.
One can also be given a prescription for the shorter-acting venlafaxine, and then one should take it two to three times per day. Usually, beginners should take Effexor at a low dose and then adjust their dosage over time based on their response.
Effexor XR should be taken in the morning or evening with food. Make it a daily habit to take a capsule at the same time. Swallow a capsule and follow it up with plenty of water. It should not be chewed or crushed.
Before Taking Effexor
One should take note of some health conditions before taking Effexor. These could interfere with the effectiveness of the drug or their safety.
- Liver or kidney disease
- Allergies to venlafaxine
- Problems with bleeding or clotting
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
- Glaucoma
- Interstitial lung disease
- Seizures
MEDvidi doctors will tell you how to properly use Effexor for anxiety. Have an online video visit today.
Is Effexor Good for Anxiety?
Certain mental health conditions may benefit from the use of Effexor XR. Because Effexor regulates emotions, sleep, stress levels, etc., it helps to alleviate panic attacks by reducing anxiety and improving a person’s mood. Effexor XR’s effects can be felt within 4-12 weeks, depending on the health condition for which it is prescribed.
However, this medication may cause side effects in some people. The majority of side effects are minor, but some can be serious. Before taking Effexor for anxiety, discuss potential side effects with your doctor so you know what to look for.
Possible Side Effects of Effexor
Effexor has some side effects, although not everyone gets them. Most normal people experience mild side effects if any at all. Some adverse effects include:
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Vivid dreams
- Weight change
- Decreased appetite
- Insomnia (difficulty falling asleep)
- Sweating (including night sweats)
- Low sodium levels
- Sexual problems
Some of these side effects may get better with time. If a person experiences persistent or negative side effects after beginning treatment, they should contact a healthcare provider.
Alternatives to Effexor for Anxiety
Some of the available alternative drugs to Effexor include:
- Cymbalta (duloxetine)
- Pristiq (desvenlafaxine)
- Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Buspirone (BuSpar)
- Alprazolam (Xanax)
- Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
- Diazepam (Valium)
- Lorazepam (Ativan)
Wrapping Up
Effexor is an antidepressant used to treat generalized anxiety disorder and other types of anxiety. Being an SNRI medication, it boosts norepinephrine and serotonin levels, which regulates mood, sleep, and alertness.
Still, Effexor has several side effects and interactions. Discussing your symptoms and health history with your doctor before using the medicine is vital. It may take up to 4 weeks to notice the benefits of taking Effexor, so one should be patient when taking this medication. If you want to know more about pharmacological treatment for anxiety and get a personalized treatment plan, contact MEDvidi doctors today.













