Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) usually presents itself
While adult patients could opt for psychotherapy or behavior training to manage the condition, medications remain the primary treatment option. In this post, let’s learn more about the ADHD medication Dexedrine—one of the commonly prescribed options. Below, we’ll review its uses, side effects, and dosages.
What Is Dexedrine and How Fast Does It Work?
Dexedrine is an ADHD medication whose effects help patients enhance focus and concentration while also decreasing impulsivity and hyperactivity tendencies. It often improves listening skills, task organization and how a patient feels resulting in increased positivity and energy.
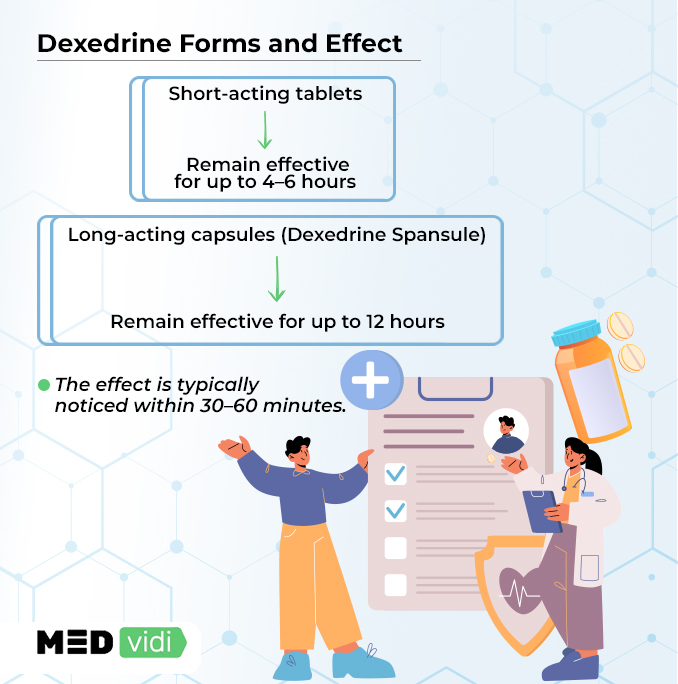
It works like other stimulant medications, increasing the brain’s neurotransmitters (dopamine and norepinephrine) by acting on the central nervous system. Typically after ingestion, it becomes effective between 30-60 minutes.
Dexedrine is available in
What Are the Common Uses of Dexedrine?
In addition to ADHD treatment, this medication can be used to treat
What Is the Ideal Dexedrine Dosage for ADHD?
Most ADHD patients that take short-acting tablets will do so two or three times daily. Each dose usually remains effective for four to six hours. For the best results, patients should take the tablets at the same time each day.
On the other hand, the Dexedrine dosage for long-acting capsules is once daily, preferably in the morning. This medication features a time-release formulation that guarantees a steady level of medication all day long (effective for 12 hours). ADHD patients should avoid taking this medication in the evening as it might interfere with good sleep hygiene.
Long-acting tablets are available in 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg doses, while the short-acting ones only have 5 mg doses. Patients should remember to follow their Dexedrine prescription instructions accurately. Most doctors prescribe the lowest Dexedrine dosage for adults with ADD at the beginning of treatment and increase it gradually based on symptoms.
In some cases, the prolonged usage of Dexedrine for ADHD in adults could lead to tolerance to the medication. Patients should assess how their dosages control symptoms and schedule regular meetings with their doctors for pertinent feedback regarding symptom management.
Who Should Avoid This Medication?
While Dexedrine is useful for ADHD treatment, it might not be suitable for patients who:
- Have allergies to dextroamphetamine
- Experiencing unresolved marked anxiety
- Have overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Diagnosed with glaucoma
- Have heart disease
- Have moderate-to-severe high blood pressure
- In an agitated state of mind
Given that amphetamines can increase blood pressure, it is always helpful to report a family history of heart issues to the doctor. During treatment, the doctor will monitor vital signs to ensure that patients remain safe.
Female patients should keep in touch with their doctors, especially if they are pregnant, nursing, or considering getting pregnant. Breastfeeding while taking medication might not be advisable as Dexedrine can affect the child.
Dexedrine: Side Effects
Typically, most patients do not experience any side effects while taking Dexedrine. However, it is important to be aware of them. Common ones include:
- Low appetite
- Tremors
- Weight loss
- Dizziness
- Sleep disruptions
- Stomach upset
Decreased appetite[4] - Eyesight issues
- Heart arrhythmias
- Seizures
Doctors could periodically ask patients to pause their dosage to monitor ADHD symptoms during treatment. Typically, the doctor will evaluate the weight, check blood pressure, and monitor any side effects of the medication. If a patient has any significant problems, they’ll need to discontinue treatment.
However, doctors advise patients who experience seizures or severe allergic reactions to stop taking medication. Also, anyone with thoughts of self-harm while taking Dexedrine should seek prompt medical attention.
Dexedrine Vs. Adderall
Both Dexedrine and Adderall are stimulant medications ideal for treating ADHD. They both have forms of amphetamine, a synthetic compound that stimulates the central nervous system.
It is important to note that this compound has two active forms: Levo(l)-amphetamine and Dextro(d)-amphetamine. Dexedrine features d-amphetamine, while Adderall has a 3:1 mixture of d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine.
D-amphetamine is considered the more potent active form, meaning that Dexedrine might be more powerful and deliver faster results than other ADHD meds. On the flip side, people looking to experience euphoric effects can abuse Dexedrine pills due to their quick stimulant effects.
Like Dexedrine, Adderall is available in short-acting tablets and extended-release (Adderall XR) capsules. However, Adderall has a wider range of available dosage forms (5, 10, 15, 20, 30 mg) than Dexedrine. The dose of Dexedrine is roughly 25% stronger than Adderall; therefore, the following formula can be applied when converting the Adderall dose to Dexedrine.
Dexedrine dose = Adderall dose × 0.75
However, any dosage conversion or switching of medication should be done under the supervision of an expert ADHD doctor.
Both Dexedrine and Adderall have the same half-life of about six hours and reach peak concentration in the body in about one to three hours. This means that the short-acting tablets require multiple doses during the day to effectively manage ADHD symptoms.
The FDA classifies both compounds as Schedule II medications, meaning these medications have a high tendency for abuse or addiction. Also, they typically share similar side effects.
Always Heed a Physician's Instructions
While this guide presents information regarding the medication Dexedrine, it should not replace your conversation with a doctor. Working closely with a prescriber ensures that patients take a holistic approach to dealing with ADHD. To consult with an experienced mental health professional, contact MEDvidi today.













