Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) was initially developed to treat emotional dysregulation experienced by people with
Everyone who wants to deal with life’s issues more effectively, in general, might genuinely benefit from knowing and acquiring the skills in DBT therapy. Let’s explore DBT and its effectiveness in treating depression.
What Is DBT Therapy?
- Helping to recognize and accept your challenging emotions.
- Enhancing your capacity to control emotions.
- Teaching how to control them and be more present in the moment.
- Helping to communicate and interact with others successfully.
- Giving the tools needed to deal with harmful behaviors and stop them.
Depression Symptoms Treated with DBT
DBT for depression strongly emphasizes patience and validation, two qualities that many depressives find lacking. When someone has depression, they frequently feel unworthy, which leads to an overpowering sensation of sadness that invalidates almost every part of their life.
DBT gives patients room to master healthy coping skills to confront their problems and eventually find freedom from them. Dialectical behavior therapy is successful in treating many
- Having trouble paying attention, thinking, or remembering
- Prolonged sadness or irritability
- Absence of interest in formerly enjoyable activities
- Recurring suicidal thoughts
- Physical symptoms such as headaches or persistent discomfort
3 Basic DBT Therapy Techniques
Dialectical behavior therapy has several techniques. Depending on the patient, their concerns, and the capacity of the person to use DBT skills for depression, the therapist may choose which technique is most appropriate for the individual.
The following are some general
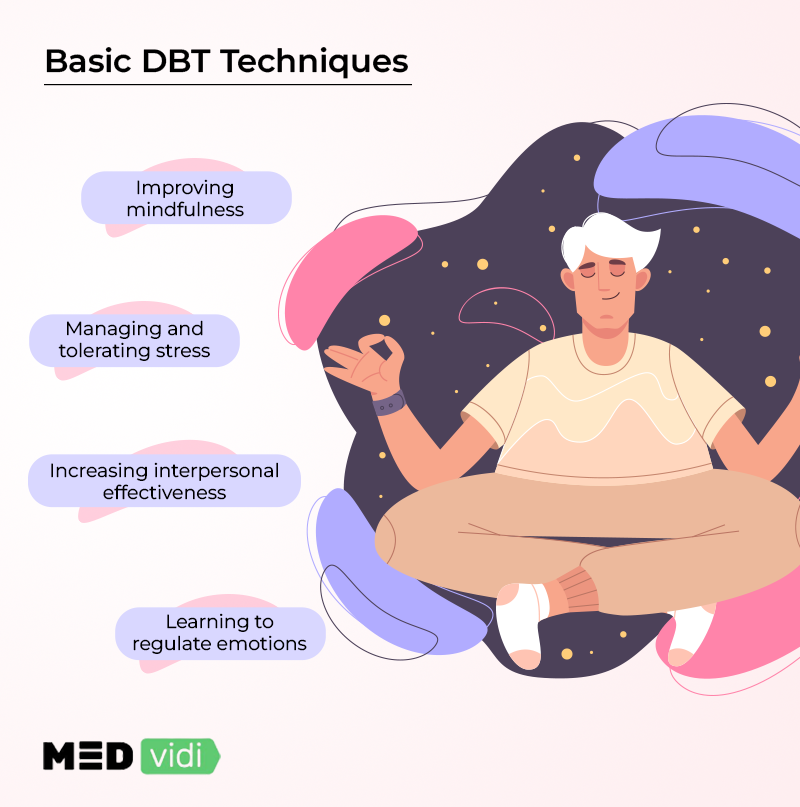
1. Emotional Control
Many people who are first recommended for DBT have extremely strong and intense emotional states (for example, suicidal patients or those with borderline personality disorder). DBT has produced a variety of activities for comprehending and controlling emotions. This frequently entails a structured approach that includes the following:
- the ability to recognize emotions, lowering one’s susceptibility to reactive behaviors that might result from emotional states.
- identifying barriers to changing emotions.
- learning to take opposite actions.
- using stress management for stress tolerance.
2. Mindfulness
Mindfulness is actually an extremely old and well-established technique in several therapy approaches. The ability to give one’s entire attention to what is happening right now while remaining nonjudgmental and experiencing the present as it unfolds is referred to as mindfulness. Although it is a skill that takes much more effort than one may think, this exercise enables one to evaluate and analyze occurrences in their environment with objectivity.
3. Tolerating stress/distress
DBT intervention aims to help clients accept stressful and painful situations without being judgmental. As a result, they may accept more constructive criticism and act more constructively to address problems within their control. For instance, while previous events, like the death of a loved one, are beyond our control, we may learn to limit the stress they cause. In several variations of cognitive behavioral therapy, including DBT, the use of stress management techniques is commonplace.
In Conclusion
DBT programs for depression can assist you in controlling unpleasant feelings and creating useful coping mechanisms for whatever difficulties you may be experiencing. You’ll attempt to strike a balance between acceptance and transformation with the aid of your therapist. MEDvidi offers personalized treatment plans for depression, and DBT therapy can be a good treatment option for depression.













