Anxiety can be an all-encompassing issue that can affect anyone, regardless of their background or lifestyle. To effectively address it, understanding the triggers that fuel
In this article, we delve into the diverse factors that can heighten anxiety levels. We also provide examples of practical strategies that may help regain emotional balance. These include lifestyle adjustments and coping techniques that can supplement your treatment plan for an anxiety disorder.
Take the first step toward managing anxiety triggers: schedule a consultation at MEDvidi.
What Are Triggers in Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety triggers are specific events, situations, thoughts, memories, or stimuli that initiate the body’s fight-or-flight response. These triggers activate the body’s
Each person’s triggers are unique, as they are influenced by personal histories and life experiences. What may be a trigger for one individual might not affect another in the same way. Also, triggers can manifest in various ways, ranging from subtle emotional discomfort to full-blown panic or outbursts. They can emerge suddenly or build up over time, making it difficult to predict or control them.
10 Common Triggers for Anxiety Attacks
Health Issues
Health issues, whether chronic or acute, can significantly contribute to anxiety. The uncertainty, pain, or disruptions caused by illnesses can trigger feelings of helplessness and fear. Additionally, the fear of developing or deteriorating health conditions can worsen anxiety in individuals already prone to excessive worry.
Medications
Certain medications, especially stimulants or those affecting the central nervous system, can trigger anxiety as a side effect. It is essential to discuss any concerns about medication-related anxiety with a healthcare provider. Sometimes, it is necessary to explore potential alternatives or adjust the treatment regimen.
Caffeine
Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and sodas, can
Skipping Meals
Skipping meals can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels, potentially triggering symptoms of anxiety. Maintaining a balanced diet with regular meals and healthy snacks can promote stable blood sugar levels and aid in anxiety management.
Negative Thinking
Negative thinking patterns, such as catastrophizing or excessive worrying, can fuel anxiety. The mere fear of experiencing a panic attack can be sufficient to trigger one for certain individuals. Recognizing these cognitive distortions and challenging them with positive affirmations or rational thoughts can help reduce anxiety’s intensity.
Financial Concerns
Financial stress and uncertainty about money matters can increase anxiety. Creating a budget, seeking financial advice, or talking to a counselor can help alleviate some of the anxiety related to financial concerns.
Parties or Social Events
Social events and parties, public speaking, performing on stage, or being in the spotlight can be anxiety-provoking for individuals with a social anxiety disorder. The fear of judgment or embarrassment in social settings may lead to heightened anxiety. Practicing public speaking or performance skills and challenging negative self-beliefs can ease anxiety in such situations.
Conflicts
Conflicts with others or within oneself can increase stress levels and lead to intense anxiety. Learning effective communication skills and conflict resolution techniques can help reduce the impact of conflict-related triggers.
Stress
Stress triggers anxiety, so work, school, or family responsibilities can act as a pervasive trigger for anxiety attacks. Engaging in stress-reduction techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness, or hobbies, can provide relief from stress-induced anxiety.
Parties or Social Events
Individuals may have specific triggers rooted in personal experiences or traumas. These triggers are highly individualized and require personalized coping strategies, such as therapy or support groups.
Ask our healthcare providers how to cope with anxiety triggers effectively in your particular situation.
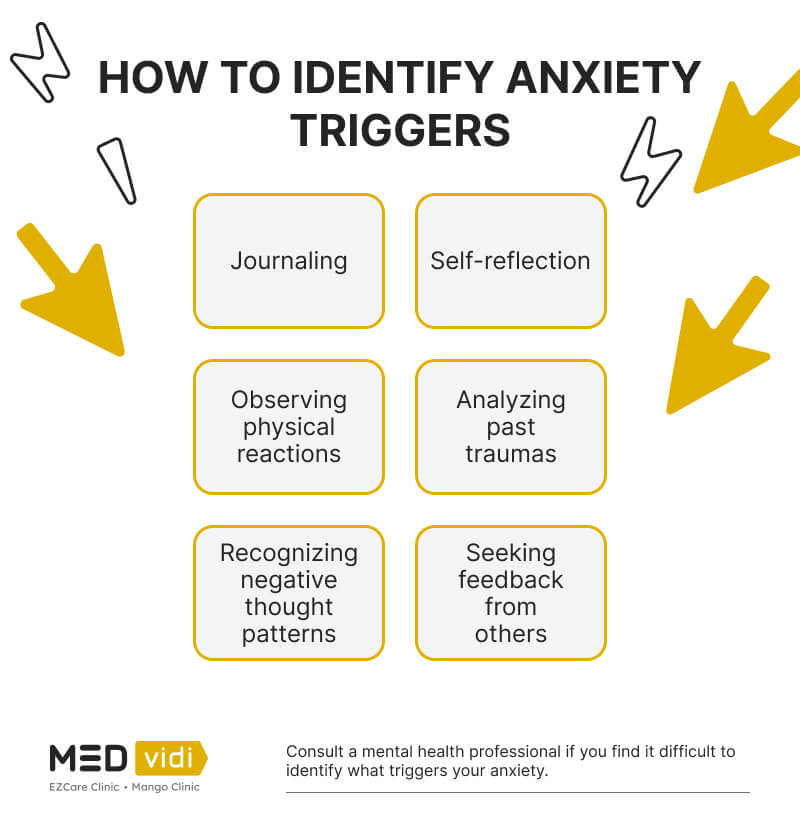
How to Identify Your Triggers
If you know what may worsen your anxiety or cause a panic attack, you can use preventive measures and lessen the impact of the trigger. Psychologists and counselors can help you define these situations and thoughts, but you can also start by yourself. These are several strategies to help you with understanding and identifying anxiety triggers:
- Self-reflect. Carve out time in your day for introspection, away from distractions, to gain clarity on your emotional experiences. Explore the past and present to uncover recurring patterns in your emotional responses to various situations or events.
- Keep a trigger journal. Maintain a trigger journal to record your emotional experiences and the circumstances surrounding them. Take note of any specific events, thoughts, or feelings that stand out during emotional episodes. Regularly revisiting your journal can reveal patterns and common denominators in your triggers, offering a deeper understanding of what initiates your emotional reactions.
- Observe your physical reactions. Our bodies often send signals when we encounter triggers. Pay close attention to physical cues such as increased heart rate, muscle tension, or stomach discomfort. These somatic reactions can be valuable indicators of underlying emotional triggers.
- Seek feedback from others. Reaching out to friends, family, or colleagues can provide valuable insight into your triggers. Ask for honest feedback on how you respond to certain situations or stressors. These external perspectives can offer a different angle on your emotional triggers that you might not be fully aware of.
- Identify past traumas and unresolved issues. Past traumas and unresolved emotional issues can be potent triggers for present-day reactions. Reflect on your past and consider seeking professional help to process and heal from traumatic experiences. Resolving past wounds can diminish the impact of these triggers on your emotional well-being.
- Recognize negative thought patterns. Negative thought patterns can perpetuate emotional triggers. Be attentive to your internal dialogue and identify recurring negative beliefs or self-criticism. Once recognized, work on reframing these challenging thoughts with positive self-talk, affirmations, and rational thinking.
- Analyze social interactions. Social interactions can be triggering for many individuals, particularly those with social anxiety. Analyze your emotional responses to social events or encounters, and identify specific situations that evoke severe anxiety or stress. Understanding these triggers can aid in developing coping mechanisms for navigating social settings more comfortably.
- Pay attention to time and environment. Triggers can be context-dependent, varying based on time, place, or the people around us. Pay attention to specific environments or situations where you experience heightened emotions. Identifying these contexts can help you prepare mentally and emotionally to deal with anxiety triggers.
Tips for Preventing and Managing Anxiety Triggers
Since it is not always possible to avoid anxiety triggers (sometimes it can cause even more stress), it is important to learn how to cope with them. Here are a few practical tips that may empower you to manage your anxiety and navigate life’s challenges with resilience and inner strength:
- Adopt healthy lifestyle habits. Regular
exercise[4] , a balanced diet, and adequate sleep contribute to emotional stability and resilience. Physical well-being is closely linked to mental health, so prioritize self-care to overcome anxiety triggers. - Limit caffeine and alcohol intake. Both caffeine and alcohol can boost anxiety symptoms. Limiting or avoiding these substances can help you maintain a more balanced emotional state and reduce the risk of triggering anxiety attacks.
- Develop self-awareness. Pay attention to your emotional responses and physical cues during stressful situations. Journaling can be a helpful tool to track triggers and emotions associated with them, thus offering valuable insights into your individual triggers.
- Practice mindfulness and grounding techniques. Incorporate mindfulness and grounding techniques into your daily routine. Mindfulness helps you stay present, allowing you to acknowledge and release anxious thoughts without getting entangled in them. Grounding exercises, such as focusing on your senses or using breathing techniques, can help anchor you during anxious moments and prevent escalation.
- Prioritize relaxation and stress-reduction techniques. Whether it’s through meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature, regular relaxation helps lower overall stress levels and enhances emotional well-being.
- Challenge negative thoughts. Learn to challenge negative thought patterns that fuel anxiety. Replace self-critical thoughts with positive affirmations, and remind yourself of past successes in managing anxiety attacks. Reframing your thoughts can empower you with a more optimistic outlook on life.
- Establish healthy boundaries. Setting healthy boundaries is crucial to getting over anxiety triggers. Learn to say no to overwhelming commitments and create a space for self-care and relaxation.
- Develop coping strategies. Identify healthy coping strategies that work for you. Engaging in creative activities, practicing yoga or meditation, or seeking support from loved ones can be effective ways to cope with stress and anxiety. Find what brings you comfort and make it a part of your routine.
- Gradual exposure to triggers. If avoiding anxiety triggers is not possible, consider gradual exposure under controlled circumstances. Gradually facing your fears can desensitize your body’s response and reduce the intensity of anxiety attacks over time. However, only do this with the guidance of a mental health professional if you find it too challenging to do it alone.
- Seek professional support. If anxiety attacks and anxiety trigger points significantly impact your day-to-day life, consider seeking professional support from a therapist or counselor. A professional can offer personalized coping strategies and help you navigate through challenging emotions more effectively.

Feeling Anxious for No Reason: What to Do?
Experiencing feelings of anxiety for no apparent reason can be both confusing and distressing. It’s not uncommon to suddenly feel anxious without any specific trigger or identifiable cause. This phenomenon is a generalized anxiety disorder often referred to as “free-floating” or “unexplained” anxiety. In such instances, the body’s stress response system may become activated without an external threat, leading to physical and emotional anxiety symptoms.
Understanding that feeling anxious for no reason is a valid and common experience can provide reassurance, and encourage you to seek support from loved ones or mental health professionals. They will help you explore effective coping strategies and potential underlying factors contributing to these anxious feelings.
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding anxiety triggers is essential in navigating the complexities of anxiety and fostering emotional well-being. Remember that seeking support from mental health professionals and loved ones is crucial in this journey, as it provides valuable guidance and encouragement. Experienced healthcare providers at MEDvidi are here to offer personalized recommendations and effective treatment options, including prescribing medication if necessary.
FAQ
What does an anxiety attack feel like?
An anxiety attack can feel incredibly intense, overwhelming, and frightening. Common physical symptoms include a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, trembling, and sweating. Emotionally, you may experience a strong sense of fear, panic, or a feeling of losing control. Some individuals might also feel disconnected from reality or have a fear of going crazy or dying during an anxiety attack.
How do you calm an anxiety attack?
To calm an anxiety attack, focus on deep breathing, inhaling slowly through your nose and exhaling through your mouth. Ground yourself by engaging your senses and bringing your attention to the present moment. Challenge negative thoughts, and consider seeking support from a trusted person or a mental health professional if needed.
How do I get rid of anxiety triggers?
To effectively manage anxiety triggers, start by identifying the specific situations or stimuli that cause heightened stress or panic attacks. Once you recognize your triggers, work on developing coping mechanisms, such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness techniques, or engaging in relaxing activities.
Gradually exposing yourself to the triggers in a controlled manner can also help desensitize your response over time. However, if triggers significantly impact your daily life, seeking guidance from a mental health professional can be beneficial for long-term relief.
Why is my anxiety worse at home?
A few factors can worsen anxiety at home. First, being in a familiar environment can make you more attuned to potential stressors and trigger occasional anxiety. Second, home may be associated with responsibilities and pressures, contributing to heightened anxiety. Additionally, the lack of external distractions at home might lead to overthinking and increased focus on anxious thoughts.
Identifying the specific reasons behind your heightened anxiety at home can help you develop coping strategies and direct you to seek support if needed.
How do you know if your anxiety is triggered?
You can tell if your anxiety is triggered by paying attention to certain signs and sensations. Common indications include an abrupt increase in heart rate, shallow breathing, feeling tense or restless, excessive worry or fear, and a sense of impending danger or doom.
You may also experience sweating, trembling, digestive discomfort, or difficulty concentrating. Understanding these patterns can help you to control anxiety triggers.













