Do you constantly worry about your health? Do you frequently visit different doctors to seek assurances about your symptoms? Do you repeatedly insist on getting your blood tests and scans done?
If that is the case, you might be suffering from a condition known as an illness anxiety disorder (IAD). It is a psychological disorder recognized by the medical fraternity as a separate diagnosis from other mental health conditions. Its characteristic features include excessive and constant worry about one’s health and unrealistic fear of having or developing a serious medical condition. It leads to obsessive behavior that prevents sufferers from functioning normally in their day-to-day lives.
Let’s explore more about what is an illness anxiety disorder and its features.
Self-diagnosis is not a solution—tell MEDvidi doctors about your symptoms and get a legit diagnosis.
Background of Illness Anxiety Disorder
Illness anxiety disorder was formerly known as hypochondriasis. The term hypochondria was first used in classical medicine by Greek physicians. So, the word hypochondrium derives from the Greek ‘hypochondrios’, which means ‘under cartilage.’ Basically, the term means the body parts between the ribs and the navel.
Why is that so? At that time, hypochondria was considered a physical illness that originated in the gut and traveled to the brain to cause psychological problems. Moreover, even until recent times, hypochondriasis used to mean ‘illness without a specific cause.’
In the latest edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5), the term hypochondriasis was rebuffed altogether due to its derogatory nature, and a new term, ‘illness anxiety disorder,’ was introduced. Now illness anxiety or health anxiety is listed under ‘somatic symptom and related disorders’ in DSM-5. It is one of the most complex psychological disorders to diagnose and treat due to its resemblance and overlap of symptoms with other mental health issues like OCD and generalized anxiety.
What Are the Causes and Risk Factors of Illness Anxiety Disorder?
The exact cause of developing illness anxiety disorder is unclear; however, many risk factors have been identified as potential contributing elements to the illness.
- Oversensitivity to body sensations: Some people are extra sensitive to normal physiological sensations of the body, and they may consider it a warning sign of a potentially serious illness. Common examples of these sensations include stomach gas, fast heartbeat, excessive sweating, sneezing, etc.
- Family influences: Parents who are overly cautious about their own or children’s health are more likely to offset health anxiety in newer generations. Also, a history of child abuse is linked with increased risk.
- Past illness experiences: If someone has a past traumatic experience with a medical condition or witnessed a loved one deal with a serious illness, they are more prone to become sensitive about their health.
- Stress and other anxiety disorders: Suffering from other anxiety and personality disorders and different phobias increases the risk of developing IAD. Similarly, persistent high-stress levels are another risk factor.
- Overindulgence in health-related content: Consuming too much medical content on the internet may put you at extra risk of health anxiety. This is particularly seen in medical students.
Anxiety is a normal reaction to stressors until it becomes severe and frequent and interferes with daily activities.
How Common Is Illness Anxiety Disorder?
IAD is a fairly new medical diagnosis, and its prevalence is estimated based on the previous data on hypochondriasis. Important epidemiology statistics regarding illness anxiety disorder are:
- Patients previously diagnosed with hypochondriasis also have a 25% chance of being diagnosed with illness anxiety disorder.
- The prevalence of IAD is about 0.1% in the general population and about 0.75% in a clinical setting.
- Adolescents and adults aged between 25 to 35 are more likely to suffer from IAD.
- IAD tends to get worse with age.
- IAD is equally common in men and women with no gender predisposition.
- People with less education and low income are at a greater risk of IAD.
Source:

Has the Covid-19 Pandemic Increased the Risk of Illness Anxiety Disorder?
Undoubtedly, there is a positive correlation between illness anxiety disorder and Covid. The coronavirus pandemic has made it more challenging for people with health anxiety to cope with their symptoms. According to
The times of uncertainty make people more anxious. At MEDvidi, consult with a best online doctor for anxiety if seems to become unbearable.
What Are the Symptoms of Illness Anxiety Disorder?
The illness anxiety disorder symptoms mostly revolve around the perception of having a serious medical condition in the complete absence or presence of only minor physical symptoms. These may be a minor bruise, mild pain, or a small rash.
The following are the characteristic behavior of a person dealing with health anxiety:
- Having frim beliefs of having or being at risk of getting a serious medical condition
- Excessive worrying about minor symptoms like coughing or itching
- Fearing that normal body processes like passing gas could mean something serious
- Incessantly scouring the internet for information on causes and symptoms of different diseases
- Repeatedly checking body functions like blood pressure and temperature
- Panicking about getting a medical condition that runs in the family
- Talking about the symptoms with family and friends and seeking assurances from them
- Visiting a medical professional often or avoiding healthcare visits altogether
- Not believing in the medical reports and getting tests done from multiple hospitals and labs
- Disregarding the doctor’s opinion and getting no reassurance from their observations
- Avoiding certain places, activities, and people out of fear of catching an illness
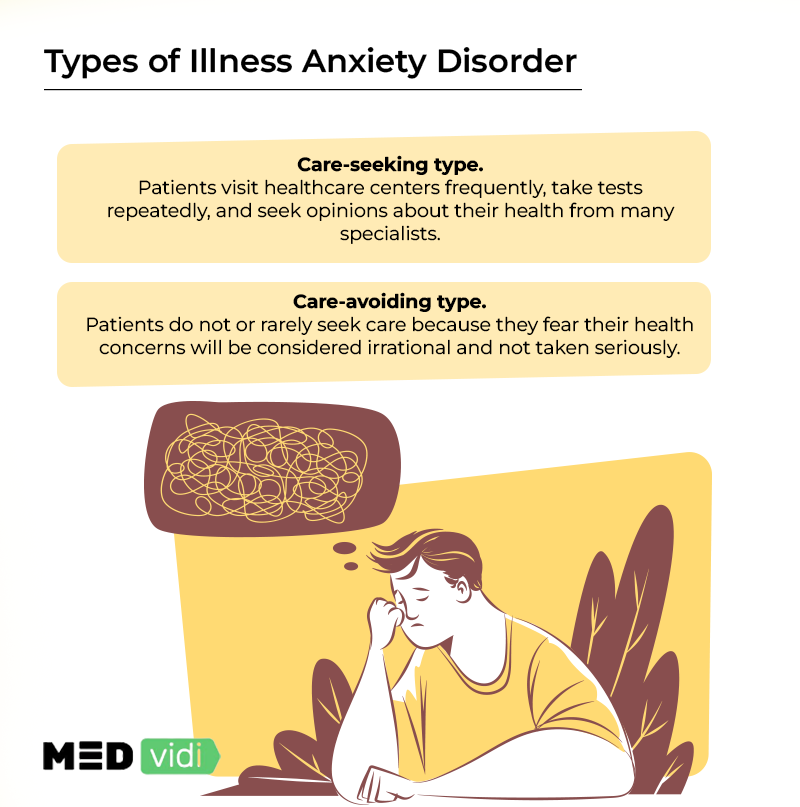
What Are the Types of Illness Anxiety Disorder?
IAD is divided into two types depending on the behavior and response of the patient:
- Care-seeking type: Individuals frequently visit healthcare centers for repeated tests and procedures and seek opinions about their health from many specialists.
- Care-avoiding type: Individuals do not or rarely use medical care because they fear their health concerns might be considered irrational and not taken seriously.
Only a certified doctor can make the right diagnosis, and MEDvidi is here to help.
How Is Illness Anxiety Disorder Diagnosed?
The first step in diagnosing illness anxiety disorder is to rule out any physical symptoms or illnesses that a person might be most worried about. After that, a comprehensive psychological exam is conducted to detect any underlying issues and comorbid conditions that might be causing the problem. Health professionals use DSM-5 criteria for diagnosing health anxiety. The following characteristic features must be present in a person as per illness anxiety disorder DSM-5 criteria:
- Obsessed with thoughts of having or getting a serious illness
- Absence of physical symptoms
- Exaggerated anxiety about personal health status
- Compulsive and redundant health-related behaviors
- Symptoms lasting for at least 6 months
- Symptoms not better explained by other mental health conditions
Researchers have also formulated an assessment tool,

How Is Illness Anxiety Disorder Treated?
Different illness anxiety disorder treatment approaches include:
Psychotherapy
Therapy is the treatment of choice for health anxiety with
Besides CBT, other therapies like exposure therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy may also be tried to deal with IAD.
MEDvidi doctors conduct a detailed assessment of symptoms and health history to develop an effective treatment plan.
Medications
Antidepressant medications are the second-line option for treating IAD. Newer antidepressants like SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) and SNRIs (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) are the most common pharmacological agents prescribed for achieving the remission of symptoms. It usually takes 4 to 6 weeks for these drugs to work and produce desired clinical effects. In case of a positive response, patients may have to take the medications for 6 to 12 months as maintenance treatment.
Lifestyle Treatment Approach
A
Self-management Techniques
Incorporating various coping skills in addition to professional treatment can speed up the recovery process and lower the recurrence of symptoms.
- Keep track of your symptoms. Record what exaggerates your health anxiety and report your triggers to the doctor. This can be achieved by keeping a journal, diary, or even a healthcare app.
- Spend time learning about how normal body sensations work and how they differ from abnormal ones.
- Engage in pleasurable and healthy activities like sports to distract yourself from intrusive thoughts about health and diseases.
- Spend more time in nature and with loved ones, away from the internet, to avoid consuming unnecessary medical information.
- Practise yoga, mindfulness, breathing exercises, and other relaxation techniques to calm your mind.
- Exercise regularly to release pent-up anxiety.
- Fix your sleep schedule with at least 6-8 hours of peaceful sleep daily.
- Eat a healthy diet by reducing sugary foods and adding fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid smoking and illicit drugs and reduce the intake of alcohol.
- Find and participate in local anxiety support group activities.
- Always consult a medical professional if you are overly worried about your health. They can guide you the best.
- Stick to your treatment plan diligently, and never be shy to discuss any of your concerns with your care providers.
Therapy or medications? Our doctors will determine what will work right for you.
What Are the Complications of Untreated IAD?
If left untreated, health anxiety can cause various problems and exponential distress:
- The increased financial burden due to unnecessary hospital visits
- Less socializing and risk of isolation
- Relationship problems with your family and friends
- Inability to concentrate and less productivity at work and in studies
- Increased risk of developing other mental health issues
How Long Does Illness Anxiety Disorder Last?
There is no specific time period regarding the duration of illness anxiety; it varies from person to person. Health anxiety episodes may come and go in cycles without any specific pattern. Usually, it is a chronic mental health condition that worsens without timely diagnosis and treatment.
Can Illness Anxiety Disorder Cause Panic Attacks?
Yes, it is common for people with an illness anxiety disorder to experience panic attacks. However, these attacks tend to subside when the primary condition is addressed.
The earlier you start treatment, the earlier you get the results. Connect with a mental health expert today.
How Is Illness Anxiety Disorder Different from Other Mental Health Conditions?
IAD is a unique mental health condition. However, it is not uncommon that it can be mixed up with other psychological issues that have some similar features. Here are some comorbid conditions associated with health anxiety:
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Somatic Symptom Disorder (SSD): People with somatic symptom disorder actually have physical symptoms that make them overly anxious about their health and the possibility of getting a serious medical illness. In contrast, people usually don’t have any physical symptoms of illness anxiety disorder.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD): The intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors are present in different areas of life compared to illness anxiety disorder, where a person is only preoccupied with health-related concerns. Therefore, health anxiety is often considered a specific type of OCD.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Anxiety and fear encompassing all areas of life characterize GAD, whereas IAD instills fears about health and diseases.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD): People with BDD have concerns that certain body features make them look ugly. However, in IAD, the concerns are related to physical symptoms, not physical appearance.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Delusion Disorder: People suffering from delusional disorder firmly believe in one or more delusions that they cannot scrape off. In contrast, in IAD, patients are willing to consider that symptoms may not be present in reality.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Conversion Disorder: In conversion disorder, patients actually have physical symptoms without any recognizable cause, which is not the case in illness anxiety disorder.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder vs. Factitious Disorder: In factitious disorder, people make up symptoms to get the doctor’s attention and diagnosis. In contrast, people with illness anxiety disorder firmly believe that they are suffering from a medical condition.
Final Words
Illness anxiety disorder is one of the most complex psychological conditions. It is tough to tackle and gets worse with time without proper medical intervention. Individuals with IAD are preoccupied with the thoughts of suffering from a serious illness without any physical symptoms. Therapy, medication, and lifestyle medicine are the most suitable treatment options for health anxiety.
Mental health experts at MEDvidi are trained professionals that provide accurate online assessment and treatment of psychological problems like illness anxiety disorder. They devise a treatment plan to deal with a patient’s major and minor individual needs. Book your online appointment now and feel the difference in your quality of life.












