SNRIs (selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are the two most widely used classes of antidepressants prescribed for various mental health problems. They belong to the new group of antidepressants that are safer and have fewer side effects than the old ones, and bring noticeable improvement in mental health.
Despite their numerous similarities, some vital differences exist in their working pattern, potential uses, side effects, and drug interactions. This article will answer questions about these medications and help you have a more detailed discussion with your doctor about which antidepressant class might be more suitable for you, SNRI or SSRI.
Feeling depressed for a long time? Contact us to get a personalized treatment plan that may consist of therapy, medications, or both.
SNRI Vs. SSRI: Overview
FDA approved SSRIs in 1987, whereas SNRIs were introduced into the market in 1993 to usher in the new era of antidepressant medications. Initially, these medications were developed to treat depression, but with continued
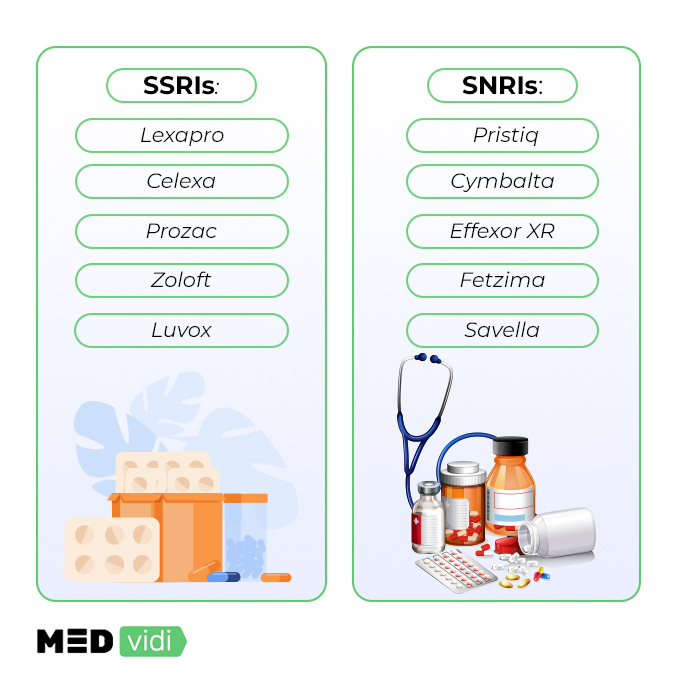
SSRIs | SNRIs |
Escitalopram (Lexapro) | Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq) |
Citalopram (Celexa) | Duloxetine (Cymbalta) |
Venlafaxine (Effexor) | |
Paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva) | Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) |
Sertraline (Zoloft) | Milnacipran (Savella) |
Fluvoxamine (Luvox) | |
Vilazodone (Viibryd) |
Overall, these new antidepressants have better tolerability, safety profile and less dosing issues. They help improve the quality of life in the long run by lowering and diminishing the symptoms of various psychological problems, including depression, anxiety disorders, phobias, OCD, PTSD, etc.
SNRI Vs. SSRI: Differences and Similarities
The key difference between SNRI and SSRI lies in their mechanism of action. SSRIs work by delaying serotonin uptake in the brain by nerve cells. As a result, more serotonin is available for a longer duration in the brain, which lessens depressive symptoms in patients.
SNRIs also follow the same principle of working with one crucial alteration. In addition to blocking serotonin uptake, they also block the reuptake of norepinephrine in the brain.
Here it is important to mention the role of serotonin in balancing mood. Serotonin is one of the neurochemicals that plays a key biological role in
In contrast, norepinephrine is vital in the body’s reaction to any emergency — fight or flight response. Whenever a person experiences intense stress for any reason, e.g., an exam, job interview, etc., the levels of norepinephrine increase in the body. It also impacts a person’s sleep, reasoning, motivation, and
Apart from these differences in their functioning, there are also many similarities between SSRIs and SNRIs, including their safety, efficacy, and duration of treatment. The following table summarizes the important aspects of SNRIs and SSRIs:
Feature | SSRIs (Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) | SNRIs (Selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) |
Differences | ||
Mechanism of Action | Targets serotonin receptors | Targets serotonin and norepinephrine receptors |
FDA-Approval | 1987 | 1993 |
Half-life | Relatively long as compared to other antidepressants | Relatively short as compared to other antidepressants |
Similarities | ||
Safety | Relatively safe as compared to older antidepressants | |
Efficacy | Comparable to older antidepressants | |
Duration of Treatment | Long (usually 6 months or more depending on the patient’s condition) | |
Dosage | Depends on the specific medication and the condition treated | |
Cost | Variable and depends on the specific medication | |
Insurance Coverage | Depends on the insurance provider | |
Available at MEDvidi | ||
Ask a mental health professional which medication will help you manage your symptoms.
SNRI Vs. SSRI: Uses
SNRIs and SSRIs are widely used in the treatment of various mental health conditions as well as in the treatment of some physical problems. Each medication in these antidepressant classes is prescribed for different label and off-label treatments.
Here’s a breakdown of different conditions treated by SSRIs and SNRIs.
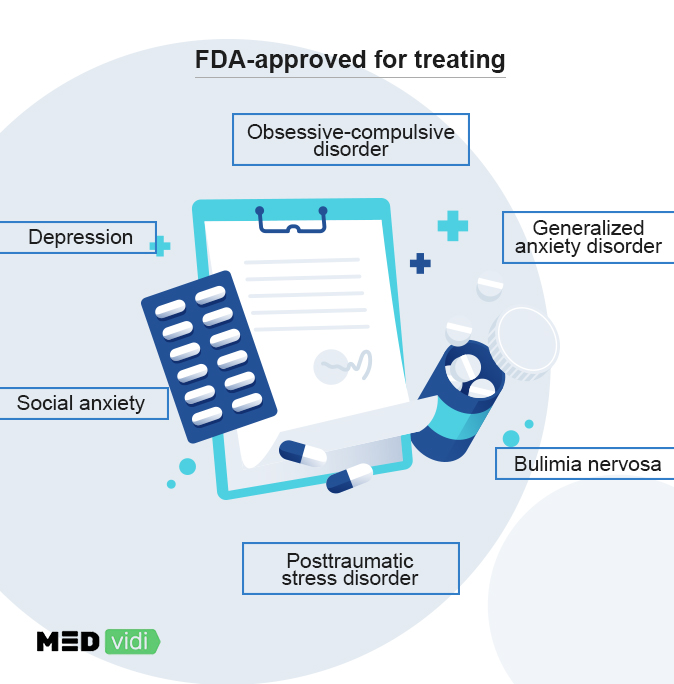
FDA-Approved Uses
Depression
All the SSRIs are recommended by the FDA to treat depression except fluvoxamine (Luvox), which is used for OCD treatment. Certain SSRIs (sertraline and fluoxetine) decrease the symptoms of depression (PMDD), associated with women’s menstrual cycle.
Currently, four SNRI drugs have the approval for depression treatment; the medication that does not is milnacipran (Savella) which is approved for treating fibromyalgia in the US. These medications are usually prescribed for moderate to severe depression because they are not as effective in the treatment of mild depression.
Panic Disorder
Both SNRIs and SSRIs are approved by the FDA to treat panic disorders associated with or without agoraphobia. Three drugs in the family of SSRIs — paroxetine, fluoxetine, and sertraline — are prescribed to manage panic disorders. These agents are especially helpful in cases of comorbid depression with panic disorder.
MEDvidi doctors are certified to prescribe SNRIs and SSRIs and will find the meds that will suit your treatment goals best.
Obsessive-compulsive Disorder
Fluvoxamine (Luvox), which is an SSRI, is specifically licensed to manage OCD in people. Along with fluvoxamine, other SSRIs, including paroxetine, sertraline, and fluoxetine, are also used for OCD treatment. The doses to treat OCD are typically higher than depression doses, and it takes a long time before their beneficial effects become evident in OCD patients. In comparison, no SNRI has been approved by the FDA for OCD treatment. However, they are prescribed off-label for this condition.
Generalized and Social Anxiety Disorder
Some SSRIs and SNRIs are used to treat generalized and social anxiety disorders and specific phobias. The choice of drug depends on the diagnosis and symptoms intensity of a specific condition. FDA has approved paroxetine, escitalopram, duloxetine, and venlafaxine for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), whereas sertraline, paroxetine, and extended-release venlafaxine are the drugs of choice for social anxiety.
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Therapy is the first-choice treatment for PTSD. However, medications may also be required to manage symptoms. For this purpose, doctors mostly recommend SSRIs, as they are effective in controlling intrusive and avoidant symptoms associated with PTSD.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia and anorexia are compulsive disorders related to eating habits and are also treated with SSRIs. In particular, fluoxetine is used for this purpose. Although psychotherapy is the treatment of choice for these disorders, adding SSRI to the management plan can help reduce binge eating and vomiting associated with bulimia.
Neuropathic Nerve Pain
In addition to mental health problems, these medications are also prescribed to manage some physical conditions. SNRIs are prescribed for controlling different nerve pains in the body. The FDA has approved
Off-Label Uses
Off-label use is defined: when a doctor prescribes a medication approved for one condition and not yet approved by the FDA to treat another condition. The SSRIs and SNRIs are used off-label for the following medical ailments.
Premature Ejaculation
SSRIs are prescribed off-label to treat premature ejaculation in men due to their anorgasmic effects. Usually, fluoxetine and sertraline are used for this purpose.
Migraines
Long-standing migraine headaches are also sometimes treated with SSRIs, especially in patients with associated depression.
Autism
Some SSRIs are prescribed to manage the symptoms associated with autism spectrum disorders.
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Duloxetine is currently under review by the FDA for approval to treat the most common type of urinary incontinence (inability to hold urine) in women — stress incontinence.
|
Condition |
FDA-Approved Use |
Off-label Use |
||
|
SSRIs |
SNRIs |
SSRIs |
SNRIs |
|
|
Major depressive disorder |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
|
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Generalized Anxiety Disorders (GAD) |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
|
Panic Disorder |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
|
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) |
✅ |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
|
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Bulimia nervosa |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Bipolar Disorder |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Diabetic neuropathy |
❌ |
✅ |
❌ |
❌ |
|
Fibromyalgia |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Premature ejaculation |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
❌ |
|
ADHD |
❌ |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Autism |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
❌ |
SNRI Vs. SSRI: Side Effects and Interactions
SSRIs and SNRIs cause similar side effects that, in turn, these side effects vary from person to person. The most common side effects of SSRIs and SNRIs include:
The most common side effects of SSRIs and SNRIs include:
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
- Problems with the gut (diarrhea or constipation)
- Problems with sleep
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight changes (increase or decrease)
The more serious side effects of these medications are disclosed below in detail.
Effects on the Heart
SSRIs and SNRIs can cause prolongation of QT intervals in the heart, leading to rhythm abnormalities in the heart. The risk is especially high in people who are also taking antipsychotic medications in addition to antidepressants. In these classes of medications, Citalopram affects the QT interval the most.
Some mental conditions have similar symptoms. Consult with a doctor to get a diagnosis and start treatment.
Headaches
SSRIs and SNRIs can cause increased incidences of headaches in patients, according to a
Seizures
Higher doses of SSRIs and SNRIs can cause
Effects on Blood
SSRIs and SNRIs cause certain blood-related problems like impairment of platelet aggregation. This may potentially lead to an excessive bleeding risk especially in the case of severe trauma. Hence, these medications are used with extra caution when taken alongside NSAIDs like ibuprofen or blood thinners, such as aspirin.
Effects on Blood Sugar and Electrolytes
These antidepressants can lower blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes. Therefore, these medications must be used cautiously in patients with blood sugar issues. Also, they can affect the levels of certain electrolytes, especially sodium, in the body, causing tiredness.
Effects on Hormones
The SSRIs can increase prolactin hormone levels, primarily associated with breast enlargement and milk production, in both women and men. The breast changes that might occur while on these medications are reversible after discontinuation of the treatment.
Extrapyramidal Effects
SSRIs can cause movement problems in patients like akathisia (inability to remain still), torticollis (neck twisting), dystonia (involuntary movements), bradykinesia (slow movements), and opisthotonos (muscle spasms).
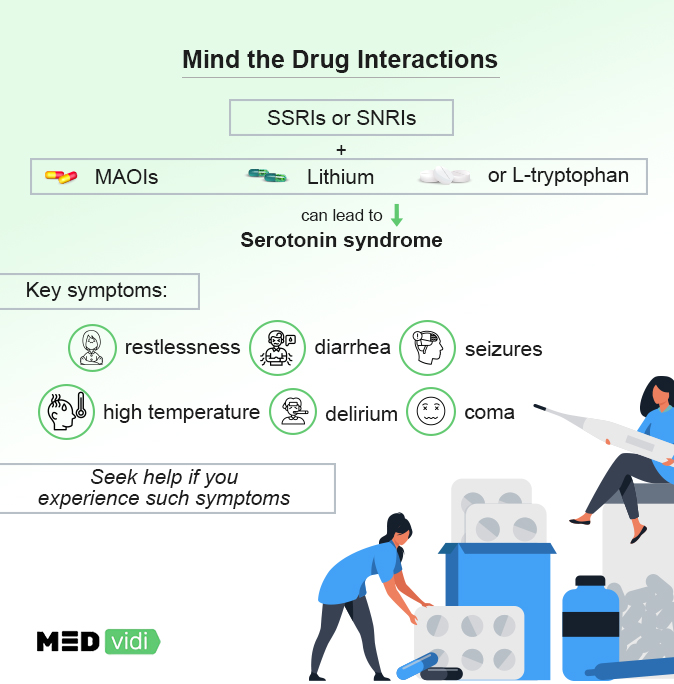
Serotonin Syndrome
If SSRIs or SNRIs are taken with other antidepressants like monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), lithium, or l-tryptophan, they can increase serotonin in the body to dangerously high levels causing a myriad of symptoms known as
- Restlessness
- Diarrhea
- Extreme nervousness
- Involuntary body movements
- High temperature
- Seizures
- Delirium
- Coma
- Cardiovascular collapse
Consult with a doctor if you have any side effects. MEDvidi professionals are there to help tailor your plan and adjust the dosage of the medications you take.
Acute Withdrawal Effects
If these medications are stopped abruptly, there is a potential for withdrawal effects. The symptoms of sudden discontinuation of these medications may include:
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Rebound depression
- Numbness
- Concentration problems
*Black Box Warning. FDA has placed some SSRIs and SNRIs (fluvoxamine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline, citalopram, and venlafaxine) on the list of medications that carry serious side effects. In the case of SSRIs and SNRIs, this warning is due to their risk of causing suicidal thoughts in children, adolescents, and young adults up to the age of 24. Therefore, these age groups are monitored very closely during the early phase of their treatment.
The table below lists the common and serious side effects associated with SSRIs and SNRIs.
Common side effects of SSRIs and SNRIs | Serious side effects of SSRIs and SNRIs |
|
|
Tell a prescriber about all the medications you currently take before an antidepressant is prescribed for you. A thorough overview allows the doctor to help you avoid potentially dangerous medication interactions.
Interactions with Other Medications
SSRIs and SNRIs are typically safe to use with other medications. Still, there are some interactions that you should be aware of and it’s imperative that you report all medications that you are taking to your doctor before commencing antidepressant treatment.
The medication interactions of SNRIs and SSRIs are similar, and the most common ones are given in the table below:
Drug | Drug Class | Possible Reaction with SSRIs and SNRIs |
Phenelzine Isocarboxazid | MAOIs | Serotonin Syndrome |
Lithium | Antimanic agents | Serotonin Syndrome |
L-Tryptophan | α-amino acid | Serotonin Syndrome |
Amitriptyline Nortriptyline | TCAs | TCA clinical toxicity |
Codeine Oxycodone Hydrocodone | Opioids | Decreased effectiveness in controlling pain |
Tamoxifen | Non-steroidal antiestrogen | Reduced effectiveness |
Ibuprofen Naproxen Diclofenac | NSAIDs | Increased risk of gastric bleeding |
Clozapine | Atypical antipsychotics | Increased risk of seizures |
Warfarin Apixaban | Anticoagulants | Increased risk of bleeding |
*For information about all the possible different interactions, consult with a doctor or pharmacist.
SNRI Vs. SSRI: FAQs
Which is better: SSRIs or SNRIs?
Many
Can you take SSRIs and SNRIs together for faster results?
SSRIs and SNRIs are relatively safe medications; however, no evidence suggests combining these can help bring faster results. Additionally, it is highly advisable to follow only your doctor’s instructions while using these medications to avoid any serious complications.
Is it possible to switch from SNRIs to SSRIs?
Yes, it is possible to switch from SNRIs to SSRIs. But before making such a change in your treatment plan, your doctor has to consider many things: medical and medication history, response to treatment, side effects, etc. Only after proper evaluation and ruling out the red flags can a doctor switch your medication from SNRIs to SSRIs.
Which is the safer medication: SSRI or SNRI?
SSRIs and SNRIs share more or less the same common side effects. No medical evidence suggests that one of them is safer than the other. The choice of medication for the treatment depends on your medical condition, medical history, and other factors like age and genetics.
Is it safe to use SSRIs or SNRIs during pregnancy?
Most SSRIs and SNRIs are safe to use during pregnancy. But paroxetine (SSRI) can increase the risk of congenital defects, especially heart abnormalities; therefore, it should be avoided during pregnancy.
How to get SSRI or SNRI prescribed?
To get a prescription for SSRIs or SNRIs, you have to first be assessed by a doctor to determine your need for any of these medications. Telemedicine has made this process much easier. You can be prescribed medication from the comfort of your home — a simple and cost-effective process without requiring you to visit a doctor’s office.
Ending Note
The above information concludes that SSRIs and SNRIs are more or less similar in their uses, tolerability, efficacy, and safety profile, with only a few minor differences. With that being said, only a qualified physician can figure out which medication is best for your condition, and this occurs after thoroughly evaluating your medical information. At MEDvidi, we have an experienced medical team that is available 24/7 to answer all your queries regarding antidepressant medications. Book your online appointment now and speak to one of our doctors if you are experiencing signs and symptoms of depression or other related mental health conditions.
To get an online consultation with a licensed prescriber, contact MEDvidi. Our mental health experts offer treatment for various mental health issues such as general anxiety disorder, depression, stress, ADHD, and other mental health problems.













