On average adults need from 7 to 9 hours of sleep. However,
Acute insomnia that lasts for a couple of days or weeks can be caused by stressful situations. What is chronic insomnia then? If sleep deprivation occurs more than three nights a week for at least three months, it could be a reason to suspect chronic insomnia disorder.
Click the button below to complete a test and check out if you need professional help.
What are the Types of Chronic Insomnia?
Chronic insomnia can be primary and secondary. Scientists are not sure what causes primary insomnia, but they think it is related to chemical changes in the brain. They study this condition with the help of specialized MRI brain scans to understand the causes of primary insomnia. Secondary insomnia results from
What Causes Chronic Insomnia?
Causes of chronic insomnia can be of different natures:
Lifestyle
- Stressful situations and changes in life
- Lack of physical activity
- Frequent napping during the day
- Irregular hours of sleep
- Jet lag caused by frequent time zones changes
- Working different shifts; working early or late shifts
- Overeating in the evening
Medical conditions
- Mental health disorders (depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, etc.)
- Medical conditions (diabetes, asthma, chronic pain, endocrine problems, etc.)
- Sleep-related disorders (restless leg syndrome, sleep apnea, etc.)
Medications and stimulants
- Certain antidepressants
- Laxatives
- Illicit drugs
- Diuretics
- Stimulants
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Nicotine
If chronic insomnia symptoms make it hard for you to function during the day, see a doctor and find out how to treat it.
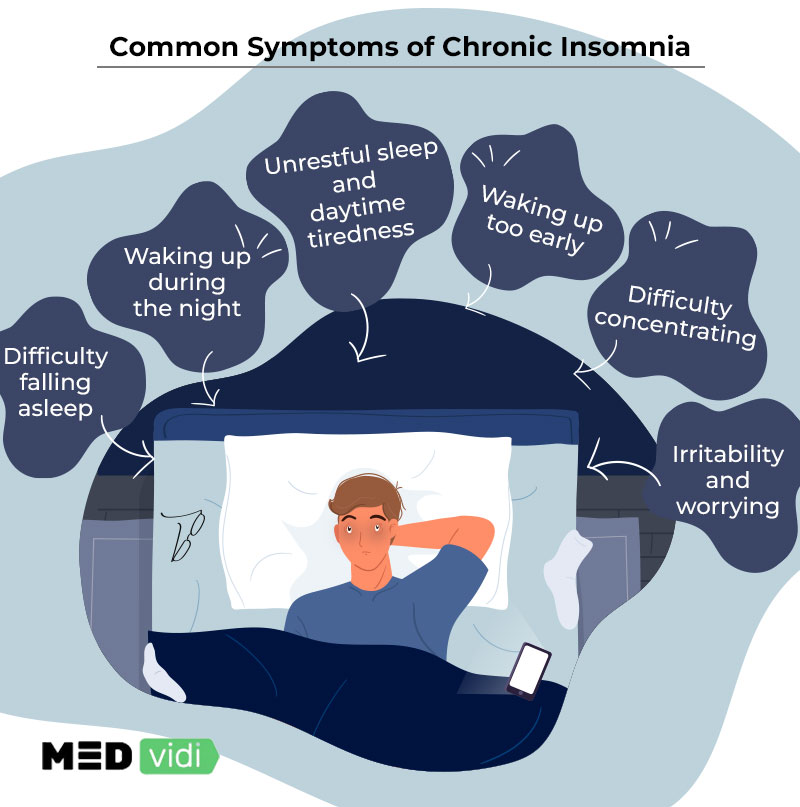
Chronic Insomnia Symptoms
People diagnosed with chronic insomnia can face the following symptoms:
- Difficulties with falling asleep
- Waking up too early
- Waking up during the night
- Inability to stay asleep or return to sleep
- Feeling tired and sleepy after getting up
- Inability to nap during the day, even when tired
- Constant fatigue
- Feeling irritated, depressed, or anxious
- Poor memory, lack of attention and concentration
- A higher number of mistakes and accidents
How to Treat Chronic Insomnia?
Treatment for chronic insomnia is personalized, depending on the causes and specific symptoms. It may include therapy, medication, or a combination of different interventions.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). According to
the research[3] , CBT is proven to be effective in treating chronic insomnia. It lets you understand how sleep habits influence your everyday life. You can learn how to change your behavior to help you sleep better. There are CBT-I techniques that are specifically focused on insomnia. - Medications. Different prescription medications (zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon, etc.) and over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids (melatonin, diphenhydramine, etc.) are available on the market. They help you fall asleep faster.
Before taking them, you should talk to your doctor about using over-the-counter sleep aids for chronic insomnia, such as chamomile tea, valerian root, and others. A consultation will help you avoid side effects or interactions with other medications.
If your chronic insomnia is caused by a medical condition, such as chronic pain or acid reflux, treating the condition may cure it.
Let our doctors help you get rid of insomnia and make your life better.
7 Self-Help Tips for Chronic Insomnia
It is also useful to follow these simple yet effective home remedies guidelines:
- Avoid using alcohol and nicotine excessively.
- Exercise regularly.
- Reduce daytime naps.
- Reduce caffeine consumption, especially in the second half of the day.
- Avoid overeating before bedtime.
- Create a dark sleep environment with a comfortable temperature.
- Sleep regular hours; set a particular time for going to bed and waking up.
Bottom Line
Sleepless nights happen in everybody’s life, but being attentive to your health is crucial in preventing severe insomnia. Track your symptoms, and if any of them start to negatively affect you, consult clinic professionals and get the help you need.
MEDvidi provides best treatment for insomnia in adults. Contact us and get a personalized treatment plan today.











