When you start taking antidepressants or discuss it with a healthcare professional, you may realize this path is not straightforward. First, the effectiveness of the same antidepressant may vary for different people. Second, its effects may not be noticeable for several weeks even if the medication suits you well. Finally, the medicine may stop being as beneficial over time. So, how to know when you have to wait and when it’s time to switch to another option because the chosen antidepressants are not working? Read on to find it out!
Evaluating Antidepressant Effectiveness: Signs to Watch For
You Feel Better Right Away
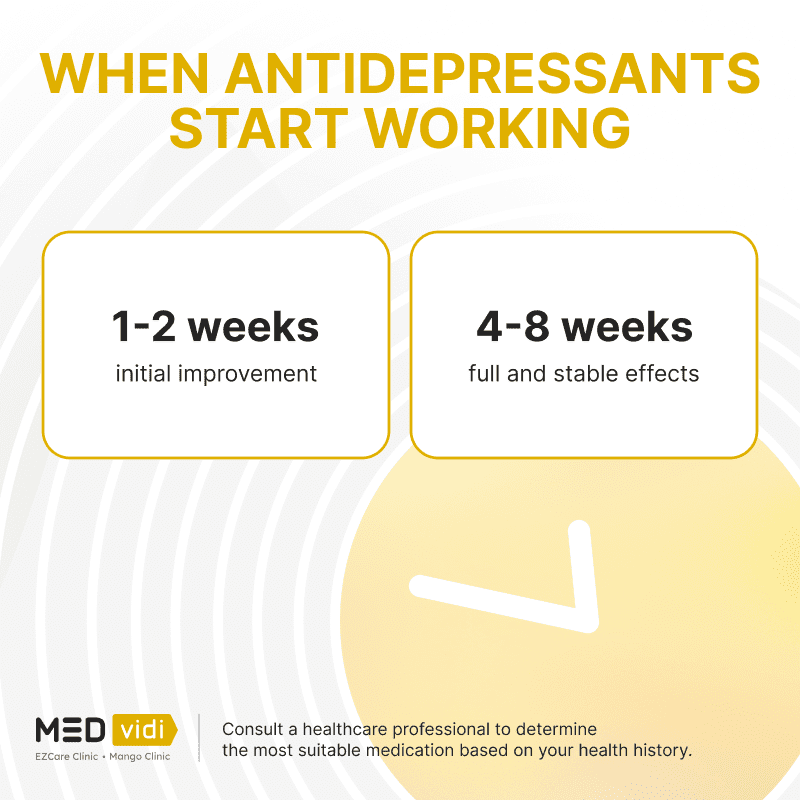
It takes up to a few weeks for antidepressants to reach a stable concentration in your body, so it’s not common for them to start working right away. If you experience an immediate boost in your mood, it might be a sign of a placebo effect rather than the medication’s therapeutic action. However, note that the impact of antidepressants is seen quicker in those with severe depression, so it may be the cause of rapid onset of action in some cases.
You Feel a Sudden Surge of Energy — Along With the Blues
A sudden energy boost and restlessness can be a sign of antidepressant-induced mania or hypomania. It happens in about
If you experience mood swings, rapid fluctuations between extreme highs and lows, it could indicate that the antidepressant is not effectively stabilizing your mood. It may also mean that you have an underlying condition such as bipolar disorder. It’s essential to reach out to your clinician and discuss this response to medication.
You Experience no Relief After a Few Months or Depression Gets Deeper
If you don’t see positive changes in
You’re Experiencing Severe Side Effects
According to a survey, 61% of people taking antidepressants experience several unpleasant side effects. The most common ones include emotional numbness, drowsiness, sexual issues, and feeling detached. These effects may fade away during the first weeks of treatment, but if you have severe adverse reactions, consult your clinician.
Suicidal thoughts may also occur, and some antidepressants have a black box warning about that. It’s important to monitor such thoughts and remember that it’s the medication’s effect, not your own wish.
What Causes Depression Medications to Stop Working?
If you notice your antidepressant is no longer working, there may be several reasons. Some of them are discussed below.
You Skipped a Dose or Several
Missing doses can lead to a decline in the medication’s effectiveness. It’s essential to take antidepressants consistently, as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
You Started a New Medication
Starting a new medicine, such as specific painkillers (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), theophylline for asthma treatment, or some others can impact the effectiveness of your antidepressant. Remember to discuss possible interactions with a healthcare professional when receiving a prescription and inform them about any new medications or herbal supplements you plan to take.
You’re Using Substances
Alcohol, recreational drugs, and even certain prescription medications can affect the action of your antidepressant. Avoid alcohol and other substances during the course of treatment since they can interfere with the medication’s desired effects.
Your Medication Was Stored Wrong
Improper storage, such as exposure to heat or moisture, can lead to a decrease in the medication’s potency. Keep your medication in a cool dry place to make sure it won’t lose its properties.
You Have Another Medical Condition
Some medical conditions can affect the way your body metabolizes antidepressants or responds to them. These include kidney and liver problems, endocrine issues, respiratory disorders, and others. If you have any changes in your health, consult with your prescriber to learn more about potential changes in the effectiveness of your antidepressant.
You’re Pregnant
Pregnancy can alter the way your body processes medication, potentially affecting the effectiveness of your antidepressant. Сonsult with your medical provider to determine if there is a need to tailor your treatment.
You’re Under More Stress
Antidepressants are not magic pills—you have to follow a comprehensive treatment plan to overcome depression. So, if you are going through significant life changes or stressful events, your symptoms can become more challenging to manage, even with medication.
You Have Bipolar Disorder, Not Depression
According to some studies, up to
You’ve Built Up a Tolerance
Over time, your body may become tolerant to the effects of your antidepressant. It means the body adapts to the medicine, so its effects become less evident. However, tolerance is more common in long-term treatment of a few years.
You’re Having Delayed Effects
Antidepressants may take several weeks to work, so the lack of positive changes in your symptoms does not necessarily show the ineffectiveness of the medication. It’s important to not stop antidepressants abruptly but consult a clinician and follow their instructions.
Three Things to Do When Your Antidepressant Stops Working
Adhere to Your Treatment Plan
Sudden discontinuation of antidepressants may cause withdrawal symptoms. This is because even though you may not notice significant effects at the very beginning of treatment, the medication already influences your body. Moreover, it may take a few more days or weeks to see improvement. It’s crucial to consult with your medical provider before making any changes to your medication regimen and stick to their recommendations.
Talk With a Healthcare Professional
A medical specialist can help assess your current treatment plan and recommend adjustments or alternative options. They may recommend switching to another medicine, using
Practice Self-care
While medication is an essential part of depression treatment, self-care still plays a significant role in maintaining mental health. A healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, sufficient sleep, regular exercise, and smoking cessation proved to
In Conclusion
Recognizing when your antidepressant has stopped working or whether it hasn’t started working in the first place is crucial. The signs can vary from the feeling of immediate improvement to severe mood swings. So, it’s also important to understand potential causes and keep in touch with your clinician. Remember to prioritize a healthy lifestyle too since it has a significant impact on the overall effectiveness of depression treatment.
FAQ
Should I take a break from my antidepressant?
When should antidepressants be stopped?
What happens if you take antidepressants for years?
Taking antidepressants for an extended period is common for chronic or recurring depression. Under proper medical supervision, it’s possible to maintain positive effects. However, some studies state that taking antidepressants for more than five or ten years increases the risk of cardiovascular problems and diabetes.
What happens if someone takes antidepressants and isn't depressed?
Can antidepressants lose effectiveness over time?
Do all antidepressants lose effectiveness over time?
When should I change my antidepressants?
How do you know if you need stronger antidepressants?
There are no specific stronger antidepressants. The need for change in your antidepressant regimen must be determined by your clinician based on your symptoms and response to treatment. If your current medication is not working properly, your provider may consider adjusting the dosage, prescribing a different antidepressant, or exploring additional treatment options.













