Insomnia is a prevalent sleep disorder that adversely affects sleep patterns. It affects approximately
A person having insomnia struggles with one or several symptoms. These may be difficulty falling asleep and sleeping through the night, having short sleep spans, waking up too early, and not being able to get back to sleep. Given that an adult needs at least seven to nine hours of sleep every day to function well, insomnia affects one’s physical and mental health.
Doctors recommend using the first line of insomnia treatment, a non-pharmacologic intervention. These include cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, and the adoption of healthy lifestyles. If the non-medication treatment does not succeed, the doctor may prescribe medication such as Ambien for insomnia treatment. In this post, let’s learn more about this drug and its efficacy.
Have you noticed any symptoms of insomnia? Consult a doctor to get best treatment options for insomnia.
What Is Ambien?
Ambien is an
Health guidelines recommend Zolpidem as a second-line treatment after a psychotherapy trial because it can cause dependence and build tolerance. In both cases, it can cause a misuse of the medication. That is why Ambien generics are DEA-controlled substances to minimize the risk of misuse and dependence and are placed in Schedule-IV drugs.
Zolpidem’s Mechanism of Action
Ambien increases the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) chemicals in the brain to boost and improve sleep. The process calms and slows activity in the brain to enable a person to fall asleep. Ambien has two versions: an immediate release and an extended-release (Ambien CR).
The immediate-release drug dissolves right after intake and aids the patient in falling asleep fast. Zolpidem extended version has two layers. The first layer dissolves right after intake to help a person get to sleep fast. The second layer dissolves gradually to keep a person asleep.
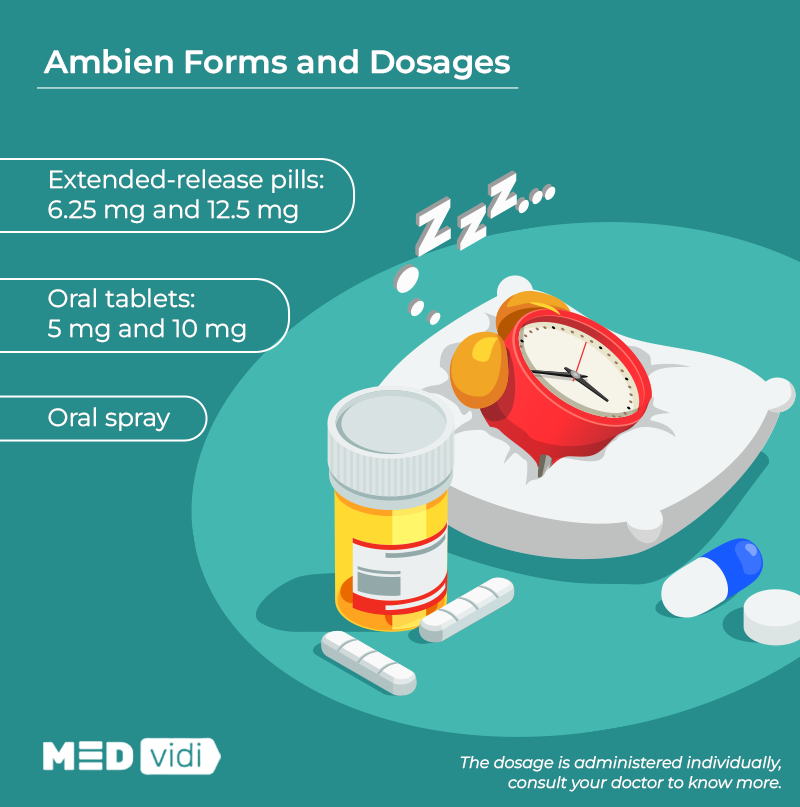
Ambien Dosage
Ambien medication is available as an oral spray, oral tablet, and an extended-release pill. Immediate-release medication is available as 5 mg and 10 mg tablets, whereas extended-release pills are available in 6.25 mg and 12.5 mg dosages. It is also available as a sublingual pill to place under the tongue and an oral spray to spray over the tongue. Depending on a person’s sleep quality, the dosage is administered in 5 mg or 10 mg tablets.
The recommended daily dose for the elderly is 5 mg; for women, 5 mg is the initial dose; and men can take either 5 mg or 10 mg. The extended-release pill is administered at a 6.25 mg dose per day, which can increase up to a 12.5 mg maximum dose. The medication is taken right before bedtime, seven to eight hours before the planned wake-up time. It is advisable not to take Ambien with or after food as it slows its effect.
Consult an online mental health doctor to know which dosage will benefit you most.
Zolpidem Contraindications
Ambien for insomnia treatment has only one contraindication: known allergy to zolpidem tartrate or any of its other ingredients. A person with any of the conditions below should also be careful to use Zolpidem for insomnia treatment only under a doctor’s guidance:
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Kidney dysfunction
- Liver disease
- Pediatric patients
- Psychotic illness
- Pregnancy
- Respiratory diseases
- Myasthenia gravis
- A breastfeeding mother
- An addiction to alcohol or substance abuse
- For safety reasons, a patient should inform the health practitioner of any other medication, vitamins, supplements, or herbal remedies he/she is using.
Precautions on Ambien Use
Some patients have had bizarre reactions to the medication in some unique cases.
For instance, some people have engaged in the following activities but do not remember after the medication wears off:
- Prepared and took meals
- Made phone calls
- Sleepwalked
- Had sex
- Sleep driven
A person should discontinue the medication and inform the doctor in case of such an experience.
Ambien Side Effects
Ambien, like most medications, may cause mild side effects, some of which do not require a doctor’s intervention.
Below are some of
- Changes in appetite, constipation, or heartburn
- Difficulty keeping balance, dizziness, or drowsiness
- Dry mouth/throat or burning/tingling of the tongue
- Headache, fatigue, or nausea
- Muscle aches, body tremors/shakes, or stomach pain
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Bizarre dreams
- Diarrhea
In case someone experiences the following severe symptoms, he/she should contact a doctor right away:
- Swollen eyes, lips, tongue, throat, or face
- Hives, rash, or itching
- Difficulty swallowing
- Breathing difficulties or shortness of breath
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Blurred vision or other sight impairments
- Chest pains or contractions of the throat
- Hallucinations
- Inability to control muscle movement
Ambien Withdrawal Symptoms
To prevent withdrawal symptoms, the doctor lowers the dose gradually. Sudden Zolpidem discontinuation after a long time of use or high doses is likely to cause withdrawal symptoms.
Ambien withdrawal symptoms include:
- Flushing
- Stomach cramps
- Nervousness
- Body shakes
- Vomiting
Seizures[5] - Panic attacks
- Hallucinations
Conclusion
Ambien, an FDA-approved short-term insomnia medication, is effective, though with many precautions on its use. For safety reasons, following the doctor’s guidelines as one takes the medication is important. In case of severe side effects, or withdrawal symptoms, it is advisable to consult a health practitioner immediately for a review.