Antidepressants are among the most frequently prescribed medications overall. Millions of people worldwide use them to treat depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. Because of the variety of available options, it’s critical to have complete knowledge of the advantages and disadvantages of each medication before making a choice.
In this post, we describe the specifics of the two commonly prescribed antidepressants: Wellbutrin vs Lexapro. They have various modes of action, indications, and side effects. Below, we compare these medicines in-depth, highlighting their similarities and differences and providing advice on picking the best medication for your requirements.
This guide will provide you with the information you need to discuss your treatment plan with a doctor, so you’ll be able to ask any questions about possible side effects and other aspects.
Uses of Wellbutrin and Lexapro
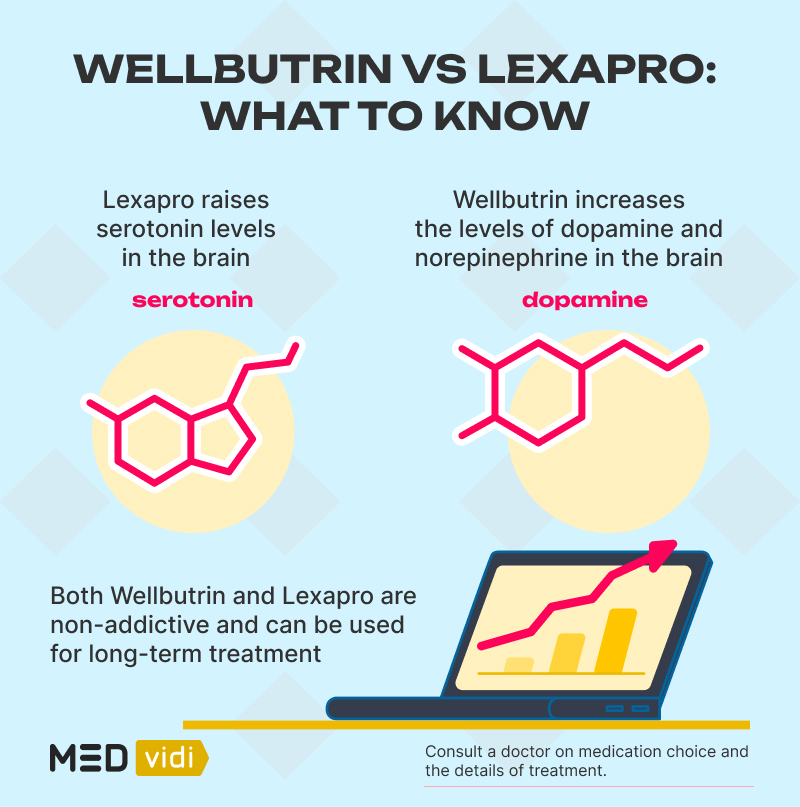
Doctors often prescribe either Lexapro or Wellbutrin for anxiety and depression. Wellbutrin (generic name: bupropion) is an atypical antidepressant that affects the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. Lexapro (generic name: escitalopram) is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain.
Here are a few typical on-label and off-label applications for both Lexapro and Wellbutrin.
| FDA-approved Uses | Off-label Uses | |
|---|---|---|
| Wellbutrin | ||
| Lexapro |
How Do Wellbutrin and Lexapro Work
Being an SSRI, Lexapro raises serotonin levels in the brain by preventing its reuptake, which increases the amount of this neurotransmitter. Serotonin is important for controlling mood, appetite, and sleep, so its increased amount helps alter the state of mind and emotions.
Wellbutrin drug class is norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs). It works by blocking the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, therefore increasing the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain and making them more available. Dopamine and norepinephrine play important roles in mood, motivation, and attention.
Lexapro vs Wellbutrin: Similarities and Differences
The following are some similarities and differences between Lexapro and Wellbutrin:
| Aspects | Lexapro | Wellbutrin |
|---|---|---|
| Drug classification | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) | Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) |
| Available forms | Oral tablets and oral solution | Oral tablets and extended-release tablets |
| Available dosages | 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg | 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, and 300 mg |
| Usual dosage | Usual starting dose is 10 mg | Usual starting dose is 150 mg |
| Mechanism of action | Increases the availability of serotonin in the brain | Inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, leading to increased levels of these neurotransmitters |
| Treatment duration | Long-term (several weeks to months) | Long-term (several weeks to months) |
| Risk of addiction | Non-addictive | Non-addictive |
| Pregnancy category | C (risk not ruled out) | B (no risk demonstrated in animal studies) |
| Contraindications | Hypersensitivity, use of MAOIs within 14 days, concomitant use with pimozide, linezolid, and intravenous methyl blue | Hypersensitivity, seizure disorder, anorexia/bulimia nervosa, use of MAOIs within 14 days, concomitant use with linezolid and intravenous methyl blue; abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and antiseizure drugs |
Typical dosage details are provided for informational purposes only. Always consult with your healthcare provider to define the most appropriate dosage for your unique situation.
Lexapro and Wellbutrin Side Effects
Both medications have potential side effects, some of which can be severe. The following are a few of the Wellbutrin and Lexapro adverse effects:
Side Effect | Wellbutrin | Lexapro |
|---|---|---|
Dry mouth | ✅ | ✅ |
Headache | ✅ | ✅ |
Nausea | ✅ | ✅ |
Insomnia | ✅ | ✅ |
Increased heart rate | ✅ | ✅ |
Hypertension | ✅ | ✅ |
Agitation or anxiety | ✅ | ❌ |
Activation of mania/hypomania | ✅ | ✅ |
Seizures (rare but serious) | ✅ | ✅ |
Risk of bleeding | ❌ | ✅ |
Drowsiness or fatigue | ❌ | ✅ |
Increased sweating | ✅ | ✅ |
Sexual dysfunction | ❌ | ✅ |
Suicidal thoughts | ✅ | ✅ |
The risk of sexual side effects is more with Lexapro than with Wellbutrin, so it can be the preferred choice in cases where sexual dysfunction is an issue.
Can You Take Lexapro and Wellbutrin Together?
Both the antidepressants Wellbutrin (bupropion) and Lexapro (escitalopram) enhance the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain in distinct ways. In some circumstances, a healthcare expert may prescribe both medications together. However, this combination should only be carried out with close supervision and under the direction of a healthcare professional.
There are a few reasons for a doctor to recommend Wellbutrin and Lexapro together. Wellbutrin, for instance, can be useful in addressing symptoms of low energy, lack of desire, and difficulties concentrating, often not treated by SSRIs like Lexapro. On the other side, Lexapro frequently works well in easing the symptoms of anxiety, which frequently co-occurs with depression.
Combining these medications, however, may raise your risk of experiencing some side effects, including agitation, restlessness, and insomnia. Patients having a history of seizures may be more susceptible to side effects from both medications because they can lower the seizure threshold.
Remember that any changes in the treatment plan, including the medications you take, their dosage, and the duration of treatment, should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
In Conclusion
Both Wellbutrin and Lexapro are frequently recommended for treating anxiety and depression. While their modes of action and potential side effects have some similarities, they also differ in some ways.
The decision between Wellbutrin vs Lexapro should ultimately be made by a healthcare professional who can evaluate the patient’s unique needs and medical background. To get personalized recommendations and an online prescription if deemed necessary, reach out to MEDvidi.













