Their inclusion does not guarantee they will be prescribed to any individual, as treatment decisions are ultimately at the discretion of healthcare providers. Healthcare providers may prescribe other medications or recommend non-pharmacological treatment based on the patient’s unique health circumstances and needs. Read more
Highlights
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) involves persistent and excessive worry that lasts at least six months and significantly interferes with everyday life.
- Symptoms of GAD include both psychological (like excessive worry) and physical problems (such as fatigue, chest pain, poor sleep, and headaches).
- GAD is treatable through a combination of medication, therapies like CBT and ACT, and lifestyle changes.
- Early intervention is important, as untreated GAD can lead to serious complications like depression, chronic pain, and insomnia.
Feeling constantly worried or on edge? Generalized anxiety disorder (medical abbreviation GAD) goes beyond just simple anxiety here and there. It’s a persistent overthinking that can affect your daily life and leave you feeling stressed and afraid. For example, you might worry every day about a job, even with positive reviews from coworkers and managers.
If worrying affects your daily life and relationships, it’s time to see a doctor or a mental health professional to get diagnosed. While this might seem overwhelming, luckily, effective, long-term treatment for GAD is possible. Below, we’ll break down the differences between GAD and normal anxiety, symptoms, and available treatments.
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Let’s explore the meaning of GAD and why it’s classified as a common anxiety disorder. Occasional anxiety is normal, but those with GAD feel a constant stream of worry, dread, or stress most days for several months or longer. Down the line, this overwhelming, excessive anxiety can affect your professional and personal life, making it difficult to keep a routine or interpersonal relationships.
Unlike normal anxiety, GAD is persistent (6 months or longer), difficult to control, and accompanied by other physical or psychological symptoms.
Is GAD common?
GAD is the most widespread anxiety disorder in the United States. It can affect anywhere between
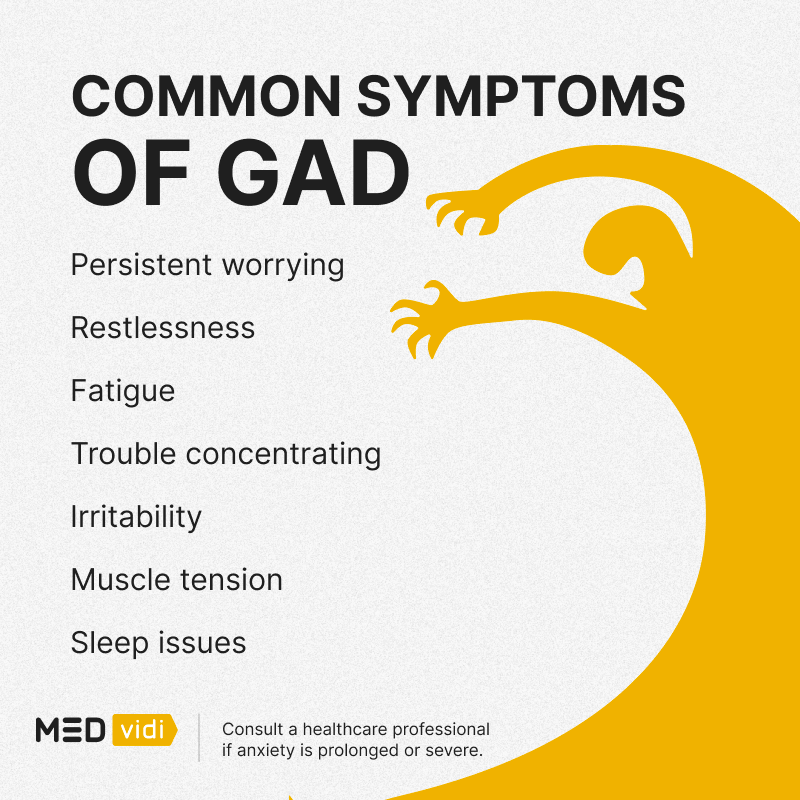
What Are the Symptoms of GAD?
It’s important to remember GAD is a type of anxiety that’s persistent; the minimum criteria for a GAD diagnosis is usually six months of continued symptoms.
- Excessive worry
- Restlessness
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Poor sleep
- Heart palpitations
- Brain fog
- Excessive sweating
- Unexplained pain (headaches, stomachaches, muscle aches)
- Using the bathroom more than normal
- Dizziness
- Trouble swallowing
- Shortness of breath

While GAD is most often diagnosed in adults, children and teens may have it too. The signs of generalized anxiety disorder in this population might include:
- Striving for perfection in school or sporting events
- Constantly looking for approval
- Avoiding school or social events
- Redoing tasks
- Seeking frequent reassurance
- Worrying about family members’ safety
Symptom severity can ebb and flow; both children and adults might feel worse during high stress periods, like relationship or school troubles, and recede during less-stressful times. You can opt for online anxiety treatment to learn how to manage your symptoms better.
What Causes Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
The exact cause of generalized anxiety disorder in adults remains unclear. However, experts have identified several potential causes for anxiety:
- Brain Make Up. No two brains are alike. GAD can be linked to issues with neurotransmitters like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin, and glutamate, among others. Medicines and psychotherapies targeting these neurotransmitters are often successful at alleviating the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder.
- Medication Side Effects. Anxiety is frequently a side effect of other medications or other mental illnesses, like substance use disorder. Before starting any medication, speak with a healthcare provider if you’re worried your medicine might cause severe anxiety.
- Environmental Factors. Sudden traumatic events, like a death in the family, abuse, divorce, or other drastic changes, can trigger anxiety. Withdrawal from addictive substances like nicotine, caffeine, and alcohol might also exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
- Other Medical Problems. Some medical conditions can cause anxiety. Those most likely to cause generalized anxiety disorder change your hormones or affect your heart/lungs. These can include hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart disease, among others.

Who’s Most At-Risk for GAD?
While anyone can get generalized anxiety disorder, you’re more at risk if you:
- Are Female. Cisgender women are more likely to be diagnosed with GAD than cisgender men.
- Have a Family History. Research suggests that
if you have a family history of GAD or similar anxiety disorders[3] , you’re more likely to get it. However, there’s no current one gene tied to anxiety. - Experienced Trauma. If you experienced trauma early in life or underwent recent life changes, your risk of mental health disorders, like GAD, is higher.
- Have an Anxious Personality. If you have an inherently nervous or anxious personality, you’re more likely to eventually be diagnosed with GAD.
How Do Doctors Diagnose GAD?
Like other mental disorders, doctors and mental health professionals use a strict set of criteria from the DSM-V to diagnose GAD. Some of the
- Constant worrying that’s difficult to control.
- Anxiety and other GAD symptoms cause “clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.”
- Anxiety is “not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition (e.g., hyperthyroidism).”
If you have GAD symptoms, your doctor might:
- Run urine or blood tests to rule out immediate medical conditions.
- Ask about your and your family’s medical and mental health history.
- Check for co-occurring mental illnesses like panic disorder and depression.
- Give you a psychological questionnaire (like the GAD-7).
Can You Self-Diagnose GAD?
While a formal diagnosis is the most accurate, you can use online anxiety tests to analyze your anxiety levels and decide whether it’s time to see a professional. These tests often use the standard GAD-7 scale, are seven questions long, and only take a few minutes to complete.
You can take this test at home, over the phone, or in person at a doctor’s office. Once you finish the test, you’ll get a score from 1-21. If it’s between 10-14, you are showing moderate GAD symptoms; if it’s 15-21, the symptoms are severe.
Note that GAD-7 alone and other online anxiety tests cannot substitute medical assessment and diagnosis.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Treatment
Since GAD comes with a wide range of symptoms, many different treatments can help. They can be broken down into traditional methods and home remedies.
Medical Treatments for GAD
- Benzodiazepines. This type of anti-anxiety medication is often used for short-term GAD relief. Benzodiazepines work by decreasing the physical symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, such as muscle tension and restlessness. Some examples include Valium, Ativan, Xanax, and Librium.
- Antidepressants. Unlike benzodiazepines, these medications are effective at treating GAD over a longer period. While they might take a few weeks or more to work, they’re non-addictive and better for long-term treatment. Some examples include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Lexapro, Zoloft, and Paxil, and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) like Cymbalta.
Before going on any medication for anxiety, speak to your healthcare provider about an appropriate prescription schedule and possible side effects.
Therapy for GAD
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT). This
type of therapy is so effective at treating GAD[5] because it helps you learn what patterns and habits lead to anxiety and how to manage them healthily. - Acceptance and Commitment (ACT) Therapy. This type of therapy focuses on teaching you
how to accept your anxious thoughts as normal[6] so you stop struggling with them constantly. ACT also helps you focus on what’s really important and how to achieve that.
Home Remedies for GAD
- Regular Exercise. Being active can help manage GAD by lowering your stress and making you feel happier. Don’t dive in all the way; start with moving your body 1-2 days a week before increasing the amount.
- Balanced Diet. Eating healthy meals with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grain carbs can help anxiety symptoms.
- Relaxation Tools.
Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing[7] are all great ways to calm physical and psychological symptoms associated with anxiety. - More Sleep. High-quality sleep is critical and allows your body and mind to heal and relax. Speak to your doctor if you’re consistently having trouble sleeping.
- Support Groups. Some people benefit from joining an online or in-person support or self-help group. Remember that any advice you hear at a support group does not replace formal treatment from a medical professional.
- Less or No Caffeine, Alcohol, or Other Substances. Avoid any harmful substance that could trigger or make your anxiety worse. Besides limiting caffeine and alcohol, avoid other drugs like nicotine and cannabis.
These self-help strategies can be used alongside medications and psychotherapy for an effective, well-rounded treatment plan. However, that’s not always possible. If you have an adverse reaction to medication or aren’t finding therapy helpful, these alternatives can still be useful on their own.

What Are Some Complications Associated With GAD?
People with GAD often have co-existing physical or mental problems. These can include:
- Low energy
- Inability to complete tasks on time
- Constant distractions
- Higher risk of depression
- Heart health problems
- Migraines
- Digestive problems like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or ulcers
- Chronic pain
- Insomnia
- Suicidal thoughts or attempts
Other mental health or mood disorders[8]
Often, getting help early can help alleviate or prevent these issues.
If you’re experiencing suicidal or self-harming thoughts and require immediate assistance, contact a crisis hotline, such as 911, 988 suicide & crisis lifeline (toll-free), or Samaritans (116-123 or via chat).
Can You Prevent GAD?
While GAD can’t be completely prevented, there are things you can do to alleviate symptoms before they get out of control.
- See a therapist or counselor after a traumatic event or experience.
- Exercise for 30 minutes 3-5 days a week.
- Don’t isolate yourself when things get tough; have a solid support system around you.
- Make to-do lists and prioritize tasks to avoid getting overwhelmed.
- Talk to a doctor before taking certain medications, especially if anxiety is a potential side effect.
- Take regular breaks and practice stress management skills.
Outlook & Supporting Those With GAD
If left untreated, GAD can leave you isolated, impaired, and unable to live your daily life. Luckily, generalized anxiety disorder usually responds well to medical treatments and at-home remedies. Symptoms will constantly ebb and flow, so stick closely to the plan and make the necessary lifestyle changes to stay healthy. If your symptoms suddenly worsen, contact your healthcare provider or dedicated support team.
If you or someone you love has GAD, there are ways to find support throughout the treatment journey. Educate yourself about warning signs, anxiety triggers, and current research. If you’re having severe symptoms of GAD, talk with someone you trust; if someone you know has this condition, or if you attend a support group for people with GAD, set aside time to discuss your experiences and share valuable tips.
How to Get Help for GAD
There are a few ways you can get professional help and treatment for GAD. First, once you notice symptoms, speak with your healthcare provider. This can be your primary care physician, a psychiatrist, or a licensed therapist/psychologist. Second, you can book an online consultation at a trusted telehealth platform, like MEDvidi.
Before your appointment, be it in-person or virtual, write out your GAD symptoms, when they started, and how they impact your day-to-day routine. Keep detailed logs of your physical symptoms, like headaches and fatigue, and list out all of your medications — this will help you complete questionnaires about your anxiety more precisely and have a more detailed discussion with a healthcare professional. In addition, be prepared to answer questions about yourself and your family’s medical history.
Based on the results of this assessment (as well as lab and health tests, if necessary), you will receive a treatment plan. It may include medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, self-help tips, or a combination of these elements. Remember to ask your healthcare provider about follow-ups to monitor your health dynamics.
Takeaway
While GAD can be overwhelming, you don’t have to experience it alone. It’s completely manageable with the help of a healthcare provider, a solid treatment plan, and a robust support system.
Remember, you’re not alone; GAD is extremely common and a wide range of treatments are available. Take steps to manage your anxiety and book an appointment with MEDvidi today to regain control of your life.
GAD FAQs
What does generalized anxiety disorder feel like?
Since GAD comes with a wide range of symptoms, it won’t feel the same for any two people. However, in general, those with GAD will constantly worry or stress out (even if there’s no clear reason). They might also have physical symptoms like headaches, tiredness, and trouble sleeping.
Does generalized anxiety disorder go away?
GAD won’t usually go away without treatment or home remedies. Thankfully, GAD does respond well to many treatment methods such as therapy, medication, and overall lifestyle changes. These will not cure GAD, but help manage the symptoms. However, you might feel brief periods of little-to-no anxiety or a more permanent, long-term period with few symptoms.
Can I live a normal life with GAD?
Of course! If you have GAD, you can live a fully enriching life once you get the right treatment. With the right tools, like medication, therapy, and a solid support system, you can manage your GAD for a long, happy life!
What are real-life examples of generalized anxiety disorder?
An adult with GAD might constantly worry about their job security, even if their performance has been reviewed positively by coworkers and managers. They might focus on small, inconsequential mistakes, feel anxious about being late to meetings or events, and struggle to decompress.
A child or teen with GAD might obsessively redo tasks, push themselves too far to be perfect in school, and avoid any social events in and out of the classroom.
Is GAD considered a disability?
GAD is a serious mental condition and can be classified as a disability if it negatively impacts your daily life and relationships. If you or someone you love has severe GAD, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides benefits and workplace accommodations.











