Mood stabilizers are a group of medications that help to deal with severe mood swings and emotional turmoil. These medicines effectively aid in managing anxiety disorders and depression since they are made to balance out emotional state. This class of medications includes lamotrigine, lithium carbonate, and aripiprazole, among many others. The choice of the most appropriate solution, the dosage regimen, and other aspects depend on the condition treated, current mood status, and other individual factors.
This article seeks to present a thorough list of mood stabilizers for depression and anxiety while explaining their mechanism of action, potential advantages and drawbacks, including common side effects, and natural alternatives.
Receive a personalized treatment plan from the health expert at MEDvidi.
What Are Mood Stabilizers?
How Do Mood Stabilizers Work for Depression and Anxiety?
While mood stabilizers are often associated with bipolar disorder, they can also be used to help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety, although this is less common. Here’s how they may be helpful:
- For depression: if different antidepressant drugs fail to help a particular patient treat depression effectively, mood stabilizers may be utilized. They target brain chemistry, which assists in regulating mood and lessens the intensity of depression symptoms. Their use improves emotional stability due to balanced amounts of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. As a result, a patient becomes less hopeless and depressed and has more energy.
- For anxiety: When other methods fail to help a patient control anxiety, mood stabilizers may be considered. They can aid in reducing excessive anxiety, agitation, and bodily symptoms. Mood stabilizers can have a relaxing effect by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, which can lessen the severity of anxious feelings and foster a stronger sense of tranquility.
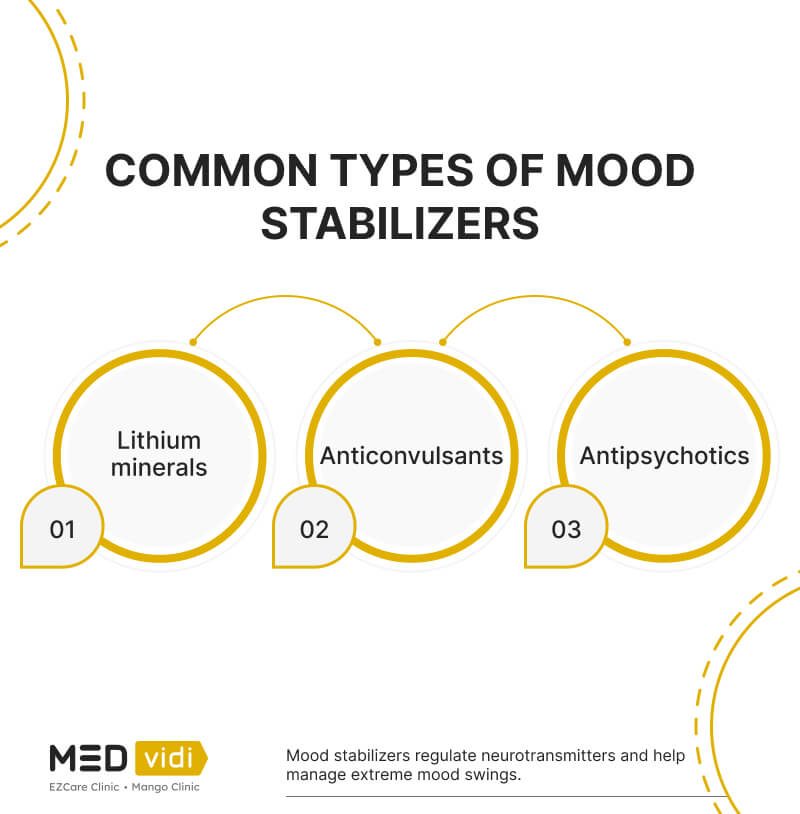
Common Mood Stabilizers
The three primary classes of medication used as mood stabilizers are lithium, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics. Within each of these groups, there are various distinct medications. Below, they are reviewed in more detail.
Lithium Minerals
Lithium is a well-known mood stabilizer commonly used to treat bipolar disorder. This substance is found naturally and comes in various forms. It works by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to manage mood changes. While it requires close monitoring of blood levels due to its limited therapeutic range, it is highly effective in preventing manic episodes.
Lithium can be prescribed as:
- Lithium citrate (Priadel, Li-liquid ).
- Lithium carbonate (Priadel, Camcolit, Liskonum)
Anticonvulsants
Originally designed to treat seizures, anticonvulsant drugs have been discovered to be useful as mood stabilizers. Anticonvulsants frequently prescribed for mood stabilization include:
- Valproic acid (Depakote): Often used for rapid-cycling bipolar disorder.
- Lamotrigine (Lamictal): Primarily used for depressive episodes in bipolar disorder.
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol): May help with manic and depressive symptoms.
Antipsychotics
In severe mood disorders, antipsychotic medicines are occasionally used as mood stabilizers. They help control manic or mixed episodes. Among the antipsychotics used to regulate mood are:
- Olanzapine (Zyprexa): Often combined with other medications for bipolar disorder.
- Quetiapine (Seroquel): Used to treat both manic and depressive episodes.
- Aripiprazole (Abilify): Can help with mood stabilization in bipolar disorder.
Take the first step toward a brighter tomorrow. Receive personalized recommendations for anxiety or depression from a certified provider,
Mood Stabilizers for Depression Treatment
Here are a few mood stabilizers that might be considered to treat bipolar depression:
- Lithium: Lithium can be effective in managing both manic and depressive episodes in bipolar disorder. It might also be used as an augmentation strategy in treating depression that doesn’t respond to other medications.
- Quetiapine (Seroquel): This atypical antipsychotic is
FDA-approved[2] as an add-on treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD). It can help alleviate depressive symptoms, especially when combined with other antidepressants. - Lamotrigine (Lamictal):
Lamotrigine[3] has been demonstrated to potentially have antidepressant effects, despite its primary purpose in treating bipolar disorder, which is to prevent mood swings. It’s frequently thought of as a maintenance therapy to stop depressive relapses. - Aripiprazole (Abilify): Approved as an adjunctive treatment for MDD,
aripiprazole[4] can be added to an antidepressant to enhance its effectiveness and alleviate depressive symptoms. - Olanzapine/Fluoxetine Combination (Symbyax): This medication combines the antipsychotic olanzapine with the antidepressant fluoxetine. It’s specifically
approved[5] for treating depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder.
Effectiveness of Mood Stabilizers
Mood stabilizers may be beneficial when anxiety and depression are linked to mood swings. These drugs contribute to mood stabilization by lessening the intensity and frequency of manic and depressive episodes.
One of the most popular mood stabilizers is lithium, which has been
Still, not everyone with anxiety and depression will be able to use or benefit from mood stabilizers. The intensity of the symptoms, the underlying causes of these disorders, and individual responses to the treatment can all affect how helpful the chosen medication is. To achieve the best outcomes, people may need to combine mood stabilizers with other medications (like antidepressants) or therapies (like cognitive-behavioral therapy).
Side Effects of Mood Stabilizers
Taking mood stabilizers can cause side effects, but not everyone experiences them. The severity of side effects can also vary. Here are some common side effects associated with these medications:
Common Side Effects | Serious Side Effects | |
|---|---|---|
Lithium |
|
|
Anticonvulsants |
|
|
Atypical antipsychotics |
|
|
Natural Mood Stabilizers
Sometimes, healthcare providers may recommend natural solutions for mood stabilization. It may be a choice for patients with mild mental health conditions, those with situational mood swings not associated with mental disorders, or those individuals who did not respond well to prescription medications. However, natural supplements serving as mood stabilizers can be used only after a consultation with a provider. Some common options are reviewed below.
St. John’s Wort
According to the National Institutes of Health, St. John’s Wort is one of the most popular dietary supplements. This herbal medicine can be helpful in managing depression, anxiety, and sleep issues. St. John’s Wort can be purchased from supplement makers in pill, tea, or liquid extract form after a consultation with a doctor.
Rhodiola
Rhodiola rosea, commonly known as Rhodiola, is a flowering plant that thrives in colder regions around the globe. It has been utilized in traditional medicine to alleviate physical and mental exhaustion, manage stress, and improve mood. Recent studies indicate that Rhodiola may possess
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are an important type of healthy fat that plays a vital role in several bodily functions. These fatty acids are typically present in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Omega-3s are well-known for their potential anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to support brain health. Research indicates that consuming more omega-3s, either through diet or supplements, may help improve mood and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)
The amino acid 5-HTP is found naturally in the body and serves as a building block for serotonin, which helps regulate mood and promote well-being. It is created from tryptophan, another amino acid that can be obtained from protein-rich foods.
Some individuals choose to take 5-HTP supplements in an effort to boost serotonin levels and potentially alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. However, the effectiveness of these supplements for treating these conditions is still being studied.
The Difference Between Mood Stabilizers and Antidepressants
Antidepressants are typically prescribed to treat depression and other related mood disorders. To assist in reducing depressive symptoms and enhancing mood, they act by modulating neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Mood stabilizers are also frequently used to treat mood-related conditions. Antidepressants and mood stabilizers are occasionally prescribed for people with bipolar disorder, although this requires close monitoring to prevent the onset of manic episodes.
Mood stabilizers | Antidepressants | |
|---|---|---|
Examples | Lithium, Valproate, Lamotrigine | SSRIs, SNRIs, Tricyclics, MAOIs, etc. |
Primary use | Manage mood swings and bipolar disorder | Treat depression and related disorders |
Onset of action | 1-2 weeks for initial effects, 4-6 weeks for significant effects | 2-3 weeks for initial effects, 6-8 weeks for significant improvement |
Association with mania | Often used to prevent manic episodes | Can trigger manic episodes in bipolar depression |
Monitoring | Blood tests and regular check-ins | Regular follow-ups for assessing effectiveness |
Final Note
The use of mood-stabilizing drugs for depression and anxiety requires careful evaluation of different factors like symptoms, treatment history, comorbid conditions, and potential side effects. A qualified healthcare provider will assess all the aspects and choose the most suitable medication. If you have bothersome symptoms and seek professional help, reach out to MEDvidi today and receive a personalized treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do mood stabilizers make you feel?
Mood stabilizers aim to stabilize mood, so, in people with bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety disorders, these medications help reduce extreme mood fluctuations. They decrease the probability of experiencing manic and depressive episodes, reduce mood swings, and therefore promote a calm emotional state.
Do mood stabilizers help with anxiety?
Mood stabilizers might help with anxiety, but they are not primarily prescribed for it. Medications like SSRIs and benzodiazepines are often used to address anxiety. Provide your healthcare provider with all the details about your symptoms and health history so that they can choose the most appropriate medication.
What mental disorders need mood stabilizers?
Mood stabilizers are primarily prescribed for treating bipolar disorder, characterized by mood swings between depression and mania. However, they can also be beneficial for conditions such as schizoaffective disorder, depression, and anxiety.
What medication is used for anxiety and mood swings?
For patients experiencing anxiety and mood swings, it is common to prescribe medications such as SSRIs (e.g., sertraline). It is essential to consult with a doctor for personalized recommendations based on individual symptoms.












