Depression is one of the prevalent mental health conditions across the globe. Statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Hard as it is dealing with the symptoms of this mood disorder, there is also the risk that it could become chronic depression if left untreated.
This article will provide an overview of the condition, starting with the definition of chronic depression, its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
Even mild symptoms of depression may interfere with day-to-day activities. Start your treatment today.
What Is Chronic Depression?
Chronic depression is a continuous and long-term form of the disease. The chronic depression definition marks out its two unique characteristics: its recurrent nature and its extended term. This condition is also known as dysthymia, but the latest Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition text revision (
To be diagnosed with dysthymic disorder, a patient must have symptoms for at least two years and should not be symptom-free for more than 2 months at any time. It is the only form of depression with symptoms that last that long. The onset of the condition is usually early in life. Generally, the patients experience mild and less severe symptoms compared to major depressive disorder. However, the condition can still cause significant disruption in all aspects of one’s life, including work, leisure, and relationships.
Only a certified mental health professional can make a correct diagnosis, Consult with MEDvidi doctors to get depression medical treatment.
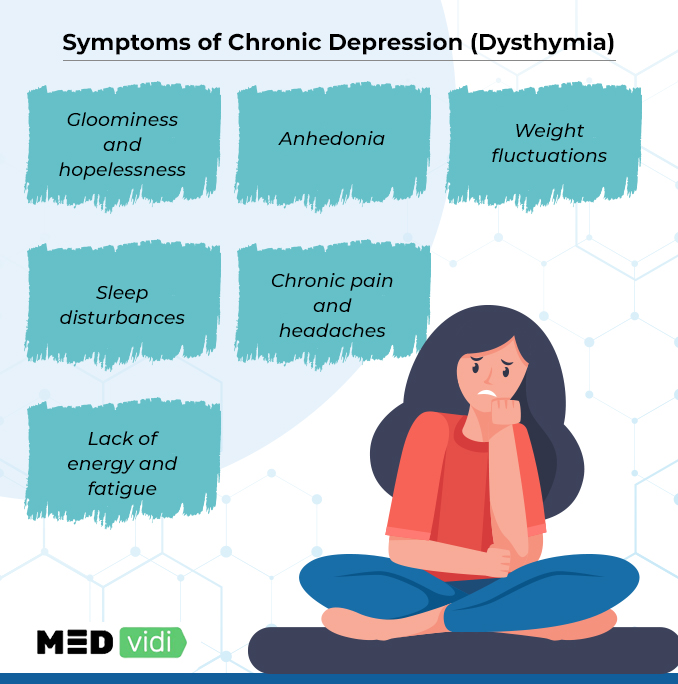
Symptoms of Chronic Depression
Chronic depression symptoms are similar to those of
- Gloominess and feelings of sadness and hopelessness much of the day every day
- Inability to have fun or enjoy things they found pleasurable
- A significant change in appetite and weight (gaining or losing more than 5% in weight)
- Sleep disturbances, either insomnia or excessive sleeping daily
- Lack of energy and fatigue across several days
- Decreased productivity and concentration
- Difficulty in decision making
- Chronic pain and headaches
- Low self-esteem
Causes of Chronic Depression
There is no one cause of chronic depression. However, experts have found
- Brain chemical imbalances: imbalances of the brain neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and glutamate, among others, can affect mood causing chronic depression.
- Genetics: the
American Psychiatric Association found[5] that a person has a 40% likelihood of developing depression if a close biological family member (sibling, parent, or child) has it. - Health conditions: some diseases, especially chronic ones, are likely to be accompanied by chronic depression. They include conditions like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Trauma, life events, and stressors: depression could be a response to a traumatic event. It could also be a reaction to a stressor or life event like losing a job, a breakup, etc.
- Medications: Certain medications like statins and birth control pills also affect the chemical balance in the brain. Depression is one of their side effects.
Are you experiencing any of the above symptoms? Go through a detailed mental health examination at MEDvidi.
Chronic Depression Treatment Options
Treatment of persistent depressive disorder follows a similar approach to other forms of depression. The treatment should always be tailored to the needs of each patient and may include:
- Psychotherapy. This treatment addresses any underlying mental and emotional causes of the condition and equips the patient with the right coping skills. The main forms of therapy are cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy, and problem-solving therapy. There is also the cognitive behavioral analysis system of psychotherapy (CBASP) under research and consideration for treating chronic depression.
- Medication. This treatment option focuses on using antidepressants to restore optimal balance and function of neurotransmitters in the brain. There are different kinds and classes of antidepressants, and one’s prescription depends on how well one responds to the drug and the severity of the patient’s depression. The most commonly prescribed antidepressants are SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) and SNRIs (serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors).
- Brain stimulation therapy. This treatment is for patients who do not respond positively to other treatments. It involves using electrical currents via
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)[6] to stimulate affected brain areas responsible for controlling your mood.
Medications and psychotherapy are the first-line options. Moreover, combining the two approaches often proves more effective.
Conclusion
It might be easy to skip out on getting medical attention at the onset of chronic depression, especially if it comes off as mild persistent depressive disorder. It is not always severe, and one may have an alternating cycle of higher or lower intensity of the condition. As such, it might be easy to accept it as part of the patient, or they may think they are getting better and not seek medical treatment. That should not be the case since it only worsens poor health, affects the quality of life one leads, and can become a lifelong depression. No one should live with chronic depression without getting medical help, so contact MEDvidi today and get personalized treatment.













